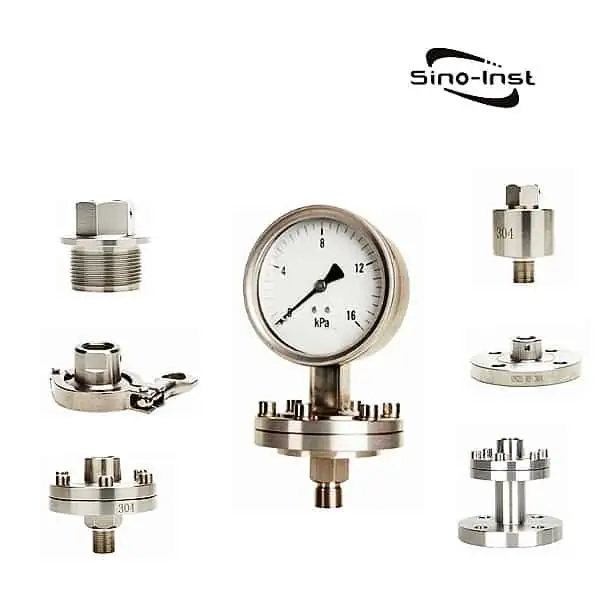
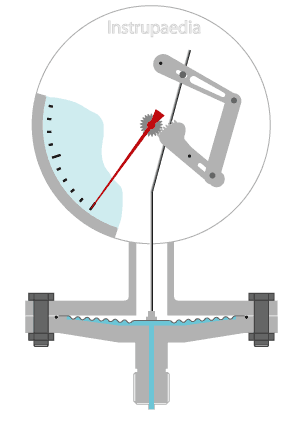
The diaphragm pressure gauge application spans from 10 mbar to 60 bar. The measuring element consists of one circular diaphragm, clamped between a pair of flanges.
The positive or negative pressure, acting on these diaphragms causes deformation of the measuring element. The magnitude of the deformation is proportional to the pressure to be measured, and it is coupled to the pointer mechanism.
Features of the diaphragm pressure gauge

- Case and wetted parts from stainless steel
- Wide choice of special materials
- High overload safety up to the 10-fold full scale value
- Process connection thread or open flange
- Scale ranges from 0 … 60bar
You may like:
Diaphragm Seal Pressure/ Differential Pressure Transmitters
Submersible Pressure Transmitter for Level and Depth Measurement
Specifications of SI-D100 Diaphragm pressure gauge
| Pressure gauges compliant with EN 837-3 | |
| Display ranges | 0…10 mbar to 0…40 bar (unfilled) 0…60 mbar to 0…60 bar (filled) |
| Nominal size | 100 mm 160 mm |
| Mechanical design | Stainless steel case with bayonet ring |
| Connections at bottom the enlarged channel opening in case of PTFE lining, optional open flange | Stainless steel |
| EN 837-3 accuracy | Class 1.6 Class 2.5 (with protecting foil) |
| Maximum pressure load Static load Dynamic load Overload | 100 % of full scale values 90 % of full scale values Up to 5-times, max. 40bar |
Connection threads and materials of SI-D100 Diaphragm pressure gauge
Type 316L pressure gauges with stainless steel connection are available with a stainless steel diaphragm (40 to 250 mbar) , or a Duratherm diaphragm (0.4 to 40 bar).
In addition, they can optionally be produced with PTFE lining.
Options of SI-D100 Diaphragm pressure gauge
- Inlet port orifice up to Ø 10 mm
- Hygienic connection,
- e.g. according to DIN 11851, DN 25 to DN 50,
- with or without lateral cleaning valve
- Other connection flanges according to former DIN standards
- Special installation or connection orientation
- Special scales such as dual ranges, fine-division (with knife-edge pointer) Stationary red pointer on the dial, or with external adjustment)
- Maximum indicating pointer, external adjustment
- Window acryl glass or polycarbonate (only for display ranges ≥ 0…100 mbar)
- Micro-adjustable pointer, mechanism aluminum
- Diaphragm with protection foil:
- PTFE (> 40 mbar, vacuum tight), sealing PTFE;
- Fine-silver (> 160 mbar, vacuum tight), sealing FPM;
- Tantalum (> 160 mbar, vacuum tight upon request), sealing PFTE, others upon request
- Up to 10-times overload protection, but max. 40 bar (600 psi) for measuring flange Ø 100 mm (3.94“) max. 2.5 bar (40 psi) for measuring flange Ø 160 mm (6.3“)
- Other filling fluid, silicone oil for temp. down to -40 °C (flange sealing PTFE)
- Version for temperatures > 100 °C
- Electrical accessories
More Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Technical Guide
Difference between bourdon tube and diaphragm pressure gauge
The working principle of the pressure gauge is through the elastic deformation of the sensitive element in the gauge. Then the pressure change is transmitted to the pointer by the conversion mechanism of the movement in the watch. Cause the pointer to rotate to show pressure. Sensitive element may be a Bourdon tube, diaphragm, bellows.
Therefore, the essential difference between the bourdon tube and diaphragm pressure gauge is the different sensitive components for pressure measurement.
Bourdon tube pressure gauge:
The sensitive element of the Bourdon tube is an elastic C-shaped tube bent into a circle with an oval cross-sectional area. The pressure of the measuring medium acts on the inside of the wave tube. In this way, the elliptical cross-section of the Bourdon tube will tend to be circular. Due to the slight deformation of the Bourdon tube, a certain ring stress is formed. This ring stress causes the Bourdon tube to extend outward. Since the head of the elastic Bourdon tube is not fixed, it will deform slightly. The amount of deformation depends on the pressure of the measuring medium. The deformation of the Bourdon tube displays the pressure of the measured medium indirectly by the pointer through the movement.
Diaphragm pressure gauge:
The sensitive element of the Diaphragm is composed of two membranes with circular waves connected together. The pressure of the measuring medium acts on the inside of the capsule cavity. The resulting deformation can be used to indirectly measure the pressure of the medium. The pressure value is indicated by the pointer. The capsule pressure gauge is generally used to measure the pressure of the gas, and it can also measure the micro-pressure and over-pressure protection to a certain extent. When several bellows sensitive components are stacked together, a large transmission force will be generated to measure very small pressure.
Bourdon tubes have the following advantages over diaphragm elements:
- They cover small pressure ranges from 0 to 0.6 bar up to high pressure ranges from 0 to 10,000 bar.
- They enable accuracies up to class 0.1 of the calibration regulations.
- They are easier to manufacture.
- They can easily be connected or sealed with the pressurised components. Depending on the material and pressure load, they are either soldered, welded or screwed to them.
Diaphragm pressure gauges are used when a Bourdon tube pressure gauge reaches its limits.
Extended reading: Pressure indicator transmitters
Frequently
Asked
Questions
More pressure measurements and applications
Small Pressure Transducer/Sensor-Low Cost-High Performance
What’s the Difference Between a Pressure Transducer and a Pressure Switch?
What Is Flush Diaphragm Pressure Transducer? When Use?
Natural Gas Pipeline Monitoring: Pressure-Temperature-Flow
Different Types of Pressure: Absolute, Gauge, Sealed Gauge and Differential Pressure
Static Pressure Sensor and Transmitter Features and Applications
Sino-Instrument offers over 50 Diaphragm pressure gauge products.
About 50% of these are Diaphragm pressure gauge, 40% are Differential Pressure Gauge, and 40% are Diaphragm Seal Pressure transmitters.
A wide variety of Diaphragm pressure gauge options are available to you, such as free samples, paid samples.
Sino-Instrument is a globally recognized supplier and manufacturer of Diaphragm pressure gauge, located in China.
The top supplying country is China (Mainland), which supply 100% of Diaphragm pressure gauge respectively.
Sino-Instrument sells through a mature distribution network that reaches all 50 states and 30 countries worldwide. Diaphragm pressure gauge products are most popular in Domestic Market, Southeast Asia, and Mid East.
You can ensure product safety by selecting from certified suppliers, with ISO9001, ISO14001 certification.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.