What is a Differential Pressure Sensor?
A differential pressure sensor is a special instrument used to measure the pressure difference between two points in a system. It contains important parts like diaphragms, strain gauges, or capacitive elements. These sensors come in different types, such as diaphragm-based, piezoresistive, and capacitive. Each with its own benefits and uses. Unlike regular pressure sensors that measure absolute or gauge pressure, differential pressure sensors specifically concentrate on the pressure difference between two points.

Differential pressure sensors are more than just another piece of machinery; they are the eyes and ears of many industrial systems, diligently measuring the pressure difference between two points in a process. By doing this, they provide invaluable insights that keep systems operating smoothly and safely. Whether in HVAC systems, medical devices, or industrial processes, these sensors are everywhere, silently playing their part.
So, why should you care about these sensors? Let’s dive deeper.
types of differential pressure sensors
Here are some common types of differential pressure sensors:
These different types of sensors offer various advantages and are used in a wide range of applications.
Working Principles of Differential Pressure Sensors
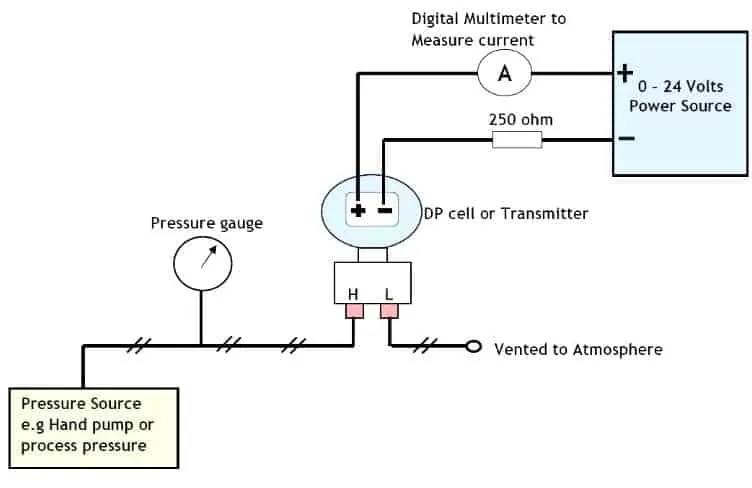
Typically, the two pressures to be measured are applied to opposite sides of a single diaphragm. The deflection of the diaphragm, whether positive or negative, determines the pressure differential.
Diaphragm-based sensors use the deformation of the diaphragm to detect differential pressure. Whereas piezoresistive sensors use strain gauges that change electrical resistance under pressure. Capacitive differential pressure sensors measure the change in capacitance caused by a pressure difference. These conversion mechanisms enable accurate and reliable measurement of differential pressure.
Some industrial differential pressure sensors use two separate absolute sensors with internal electronics to calculate and provide differential pressure.
Another way to achieve differential pressure measurement is to use two absolute pressure sensors and then calculate the difference on the industrial control system.
This is useful in situations where two different types of sensors are required due to the measured medium (i.e. liquid and gas) or the measurement environment.
The principle of differential pressure measurement states that differential pressure (also shown as DP or Δp) is the difference between two applied pressures.
For example, if the pressure at point A equals 100psi and the pressure at point B equals 60psi, the differential pressure is 40psi (100psi – 60psi).
Read more about: Different Types of Pressure: Absolute, Gauge, Sealed Gauge and Differential Pressure
Featured Industrial Differential pressure Transmitters

Extended Diaphragm Seal DP Transmitter is a level transmitter direct mounted on pipe or tank. The isolation diaphragm is in direct contact with the liquid medium.

Flange Mounted Differential Pressure Transmitter is also called single flange DP level transmitter. For liquid, gas or vapor pressure measurement.

Smart Differential Pressure Transmitter measures industrial differential pressure. Can Works with diaphragm seals, capillary, HART. Outputs standard signals (such as 4 ~ 20mA, 0 ~ 5V).

Piezoresistive Differential Pressure Transmitter utilizes the piezoresistive effect of semiconductor silicon materials. Realize accurate measurement of differential pressure.

Remote Seal DP Transmitter is often used as a tank level transmitter. The smart pressure transmitter is connected with a stainless steel flange by capillary. The pressure is sensed by a remote transmission device installed on a pipe or container.

Differential pressure (DP) level transmitter is a perfect solution for tank level measurement. Flanges, seal diaphragms, capillaries, and DP transmitter are often used to measure liquid levels.

Quickly measure the positive, negative or DP of air or non-corrosive gas. Sino-Inst supplies Differential Pressure Gauges made in China. DWYER 2000 Differential Pressure Gauges, Magnehelic differential pressure gauges are also available.
Differential Pressure Sensors Vs. Pressure Sensors
When it comes to the world of pressure measurement, two types of sensors often come into focus: differential pressure sensors and pressure sensors. Both have significant roles in various industries. But they serve different functions and have unique characteristics. Let’s dive into the key differences between them.
In conclusion, while both types of sensors serve to measure pressure, the choice between a pressure sensor and a differential pressure sensor depends largely on the specific application and requirements. Understanding these differences is the first step in determining which sensor is the most suitable for your needs.

Applications of Differential Pressure Sensors
The versatility and precision of differential pressure sensors make them highly valuable in a variety of industries. Here are 6 key ones, explained in the simplest terms:
- HVAC Systems: These sensors help control how much air is moving in heating and air conditioning systems. They also tell us when to change filters by measuring the pressure drop across them.
- Industrial Control: In factories and plants, these sensors help manage the flow of chemicals, oil, gas, food and drink by monitoring pressure changes in pipes.
- Flow Measurement: By checking the pressure drop across a blockage in a pipe, these sensors can tell how fast a liquid or gas is flowing. More about DP flow meters.
- Filter Monitoring: The sensors can tell when a filter is getting clogged by noticing a change in pressure across it. This helps in timely cleaning or replacing the filter.
- Medical Equipment: In devices like breathing machines and infusion pumps, these sensors help control the flow of air or medication to ensure the patient’s comfort.
- Tank Level Measurement: By measuring the pressure difference from the top to the bottom of a tank, these sensors can accurately tell how full a tank is, be it water, fuel, or grains. More about: Use Differential Pressure Transmitter to Measure Liquid Level.
In a nutshell, from air conditioning systems to medicine, and fuel storage to food factories, differential pressure sensors make things work better and safer. They are truly a vital part of many systems and processes.
FAQ
More Pressure Measurement Solutions
Top Digital Pressure Transducers with Display
Why Shielded Twisted Pair Cables for Industrial Instrumentation
Custom Case: Pressure Transducer Connector with 6 Pin Bendix Connector
Wetted Materials of Pressure Senors – Definition and Overview
Choose Stainless Steel Pressure Transducers
Top 5000 PSI Pressure Transducers: A Pre-Purchase Guide
Understanding the role and function of differential pressure sensors is crucial for anyone involved in fields like engineering, HVAC, industrial processes, or healthcare. They might be small devices, but their impact is huge.
Are you intrigued to learn more about how differential pressure sensors can benefit your operations? Or maybe you’re considering integrating these sensors into your own processes?
As an experienced manufacturer and supplier, Sino-Inst is here to help. So why wait? Start exploring how differential pressure sensors can revolutionize your systems today.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.
