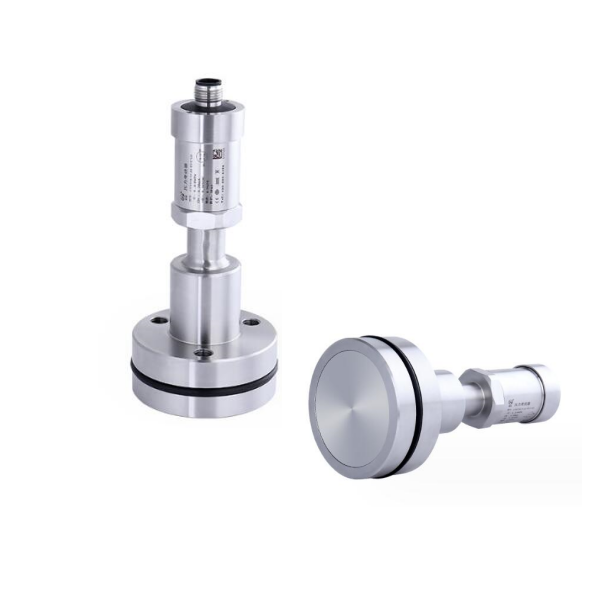
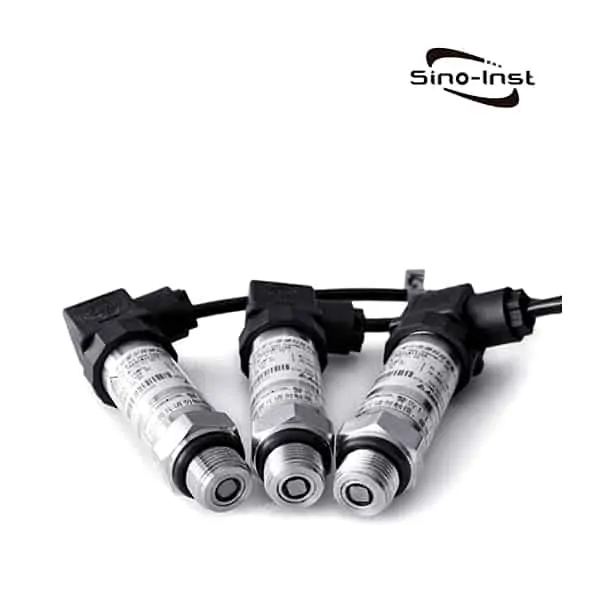
In industrial control systems, Pressure Transducers play a key role in monitoring and regulating pressure. You must have heard of 4-20mA pressure transmitter, 0-10V pressure transmitter, RS485 pressure transmitter, etc. When it comes to analog Pressure Transducers and digital Pressure Transducers, although they have the same goal – to accurately deliver a pressure signal, the technical details and practical application are very different.
Next, we’ll dive into the differences between analog Pressure Transducers and digital Pressure Transducers. Help you make informed decisions and ensure your control system operates efficiently and accurately.
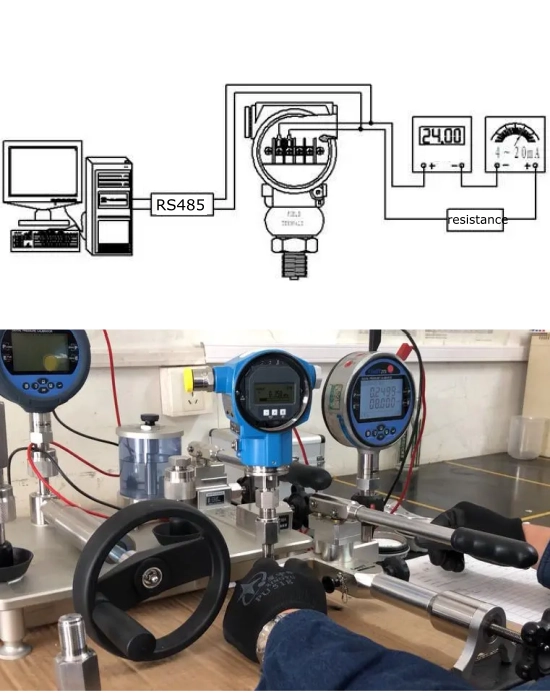
We Sino-Inst are professional pressure transmitter manufacturers. More than 50 types of pressure transmitters are available to choose from. The output signals of the pressure transmitter are available in a variety of options: mV/V, 0/5 V, 0/10 V, 4/20 mA, as well as RS485, HART, etc. We also offer multiple levels of customization to meet your needs. Including customization of installation dimensions, measurement range, explosion-proof and anti-corrosion, high temperature, low temperature, etc.
Featured Analog & Digital Pressure Transducers

Low pressure transducers for air and non-corrosive gases low pressure measurement. 0 ~ 2.5kPa to 0 ~ 30kPa measurable.

Flush membrane / diaphragm structure, anti-blocking design. Pressure measurement of viscous media.

Liquid pressure sensor is widely used for pressure measurement of various liquids. Like water or oils. IP68 waterproof.

Pressure sensor for Ultra high pressure applications. Ultra high pressures up to 15,00MPa. 0-2000MPa to 0-7000MPa (customized).Ball head M20 × 1.5, cone head M20 × 1.5.

High Temperature Pressure Sensor for pressure measurement of high temperature gas or liquid. Such as steam pressure. High temperature up to 800 ℃.

Sanitary Pressure Transmitter, also called tri clamp pressure transmitter,
is the pressure transducer with the flush diaphragm (flat membrane) as the pressure sensor.

The 4-20mA/ Voltage Pressure Transducer,
also called pressure transmitter 4-20mA,
is a pressure sensor with4-20ma/Voltage output.

Pressure transmitters for general industrial applicaitons. -0.1kPa ~ 0 ~ 0.01kPa ~ 100MPa ~150MPa. 0.1% FS, 0.25% FS, 0.5% FS. 4-20mA (2-wire system), 0-5 / 1-5 / 0-10V (3-wire system)

Digital Pressure Sensor is particularly suitable for use in computer control systems. RS485 half-duplex working mode.

Combined pressure and temperature sensor for Simultaneous measurement of pressure and temperature.
Thermocouple types: J, K, E type or PT100 platinum resistance. Two outputs do not affect each other.
More about pressure transmitters
Pressure transmitters can be divided into analog output and digital output according to the output signal. Analog output means that the output signal is an analog quantity, such as 4-20mA, 0-5V, etc. Digital output means that the output signal is a digital quantity, such as RS485, CAN bus, etc.
Analog Pressure Transducers
Analog Pressure Transducers convert mechanical pressure into continuous analog electrical signals, such as 4-20mA current or 0-10V voltage. This conversion occurs through physical pressure acting on the sensor’s sensitive element (usually a diaphragm or piezoelectric material), causing it to deform. This deformation is then converted into an electrical signal, the size of which is proportional to the pressure acting on the sensor.
The advantages of Analog Pressure Transducers are their simple structure, low cost, and durability. They typically do not require complex programming or special interfaces, making them easy to integrate with existing systems. In addition, analog signals can withstand electrical noise during long-distance transmission, which makes analog transmitters ideal for use in industrial environments with high electromagnetic interference.
Digital Pressure Transducers
Digital Pressure Transducers convert pressure information into digital signals. In terms of working mechanism, these transmitters usually contain a pressure sensor that senses pressure changes and converts it into an electrical signal, and then converts the analog signal into a digital signal through a built-in analog-to-digital converter (ADC). During this process, the transmitter will also perform signal amplification, filtering and digital processing to ensure the accuracy and stability of the output signal.
The advantages of Digital Pressure Transducers are significant. First, they provide greater accuracy and resolution because digital signals are not as susceptible to noise as analog signals.
Second, digital transmitters often have self-calibrating capabilities, reducing maintenance.
Furthermore, these transmitters can interface directly with computer systems to facilitate remote monitoring and data logging.

Analog Pressure Transducers vs Digital Pressure Transducers
Accuracy comparison
Digital Pressure Transducers: Typically provide greater accuracy. The high resolution of digital signals and their resistance to external interference. This gives digital transmitters an advantage in providing accurate readings.
Analog Pressure Transducers: Can provide relatively accurate measurements in environments without severe electromagnetic interference. However, signal attenuation may occur in long-distance transmission or high-interference environments.
Stability
Digital Pressure Transducers: In theory, digital technology can provide better stability, but special designs may be needed to protect electronic components in extreme environments.
Analog Pressure Transducers: With simple structure and mature technology, they are more suitable for harsh industrial environments, especially in high temperature, high pressure, and high vibration situations.
Responding speed
Digital Pressure Transducers: Fast response times, especially where fast change detection is required.
Analog Pressure Transducers: Relatively slow to respond, but generally adequate for most industrial applications.
Ease of use
Digital Pressure Transducers: Can integrate directly with computer systems and modern control systems to provide easy-to-understand digital readouts, but may require complex programming and configuration.
Analog Pressure Transducers: Simple to install, easy to use, no complex configuration required, suitable for users of different technical levels.
Cost-benefit ratio and long-term return on investment
Digital Pressure Transducers: The initial investment is higher, but in the long term, accurate data collection and processing increases efficiency and reduces maintenance costs, thus potentially providing a better return on investment.
Analog Pressure Transducers: Low initial cost, suitable for projects with limited budgets. While long-term maintenance costs may be higher, its stability and durability may reduce overall replacement and repair costs.
When selecting a suitable pressure transmitter, all of the above factors should be considered to ensure that performance requirements are met while maximizing cost-effectiveness within the budget.
More Pressure Measurement Solutions
- How to convert a 4-20mA to 0-10V /1-5V signal?
- What does SCADA stands for?
- What is a PID controller?
- Static Pressure vs Dynamic Pressure vs Total Pressure
- Introduction to Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
- Steam Pressure Transmitter
- Intrinsically Safe vs Explosion Proof Pressure Transmitters
- How to Calibrate a Pressure Transmitter
- Differential Pressure Transmitter Installation Guide
- Use Differential Pressure Transmitter to Measure Liquid Level
- MEMS Pressure Sensors
- Application Analysis of Intelligent Pressure Transmitter
- Differential Pressure Flow Meters
- Water Pressure Transducers
- Capacitive pressure transducer
- Pressure indicator transmitters
- How Does a Pressure Transmitter Work?
- Pressure Transmitter Calibration
When faced with choosing between Analog Pressure Transducers or Digital Pressure Transducers, the key is to understand the capabilities and benefits of each. Analog Pressure Transducers are known for their stability and cost-effectiveness, while Digital Pressure Transducers are favored for their high accuracy and ease of integration.
We at Sino-Inst not only offer a wide range of pressure transmitters, but also cover a wide range of flow, level and temperature measuring instruments. These instruments have excellent performance in the fields of crude oil flow measurement, liquid level measurement, and temperature measurement.
If you are looking for reliable pressure measurement solutions, please contact us. Sino-Inst will provide you with professional advice and customized services to help your project succeed.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.





