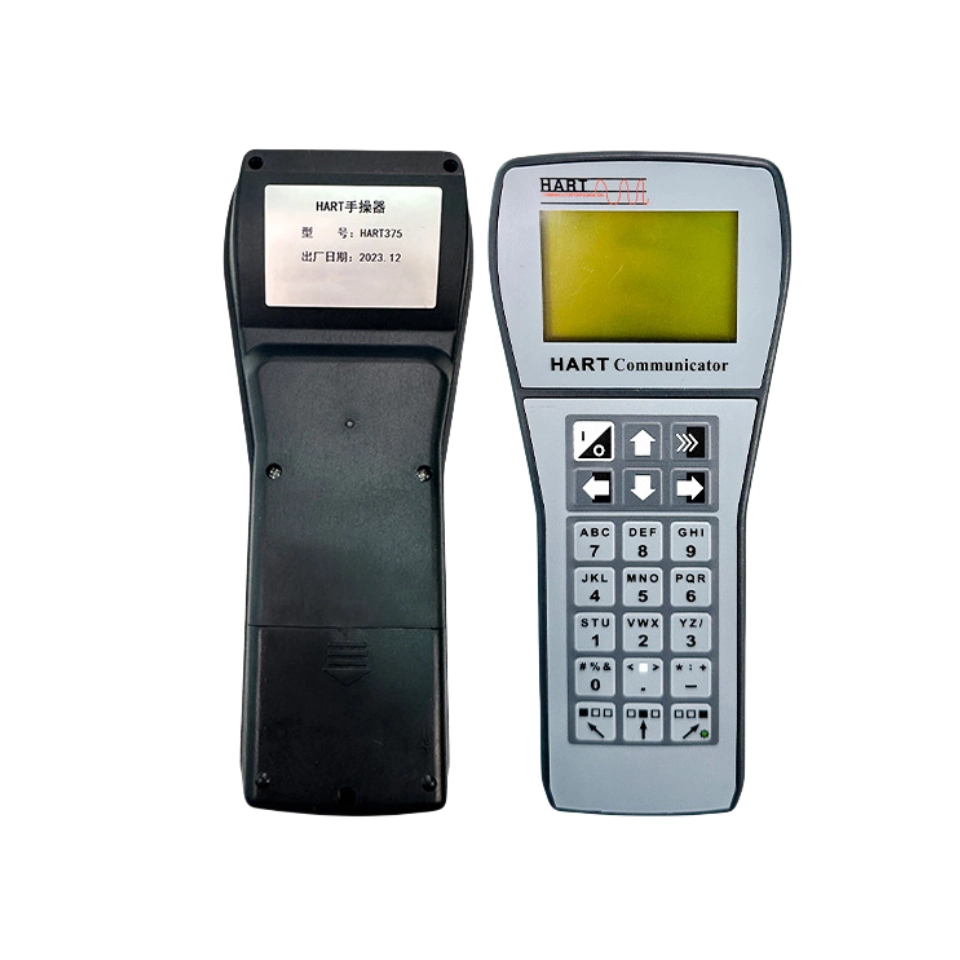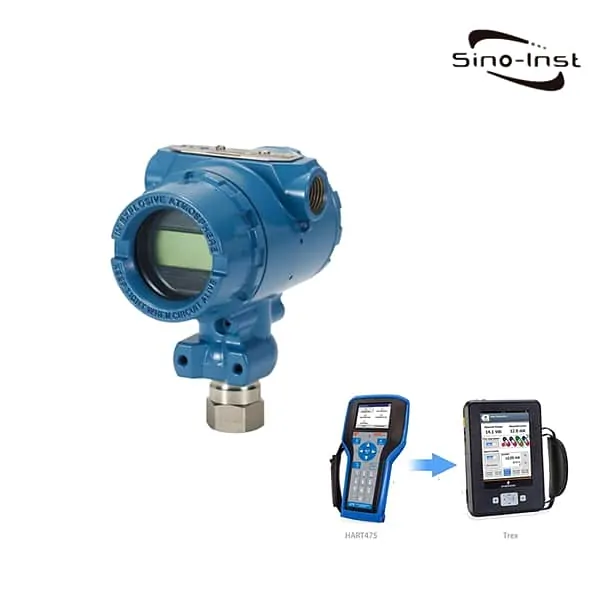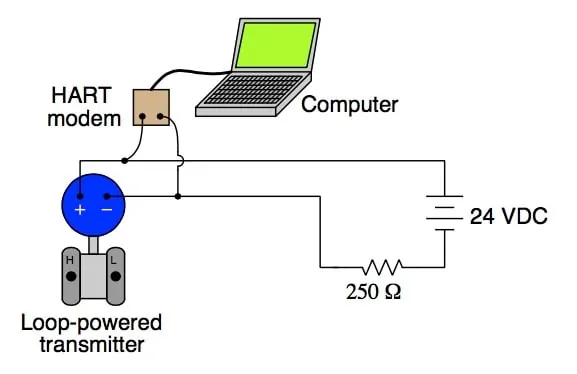
The HART protocol is the most trusted communication protocol in recent years. It combines the characteristics of analog systems and digital control systems.
Field instruments in process plants are beginning to be subject to more complex metrology regulations. Most new field instruments are now smart digital instruments. HART is widely used in process and instrumentation systems, such as smart HART pressure transmitters.
What is the HART protocol?
The full name of HART protocol is Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol. This open standard for fieldbus communication was introduced by Fisher-Rosemount in the 1980s.
In order to solve the communication problem between industrial field intelligent instruments and control systems. The FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) frequency shift keying signal based on the Bell202 standard is used to superimpose an audio digital signal with an amplitude of 0.5mA on the traditional 4-20mA analog signal for two-way digital communication.
HART communication will not interfere with the analog signal transmitted to the control system. It ensures compatibility with existing analog systems. It is a transitional product in the process of transforming from analog systems to digital systems.

Benefits of HART protocol
Compatibility: HART protocol can be used to connect all types of field instruments, including temperature, liquid level, pressure, flow, analyzer, etc.
Reliability: HART protocol has full-duplex communication capability. The device can send and receive at the same time, ensuring the reliability of communication.
Ease of use: HART protocol can be transmitted through the existing 4-20mA signal. No additional hardware and cables are required, which is easy to use.
Working principle of HART protocol
HART protocol usually uses 4-20mA signal for two types of communication: analog signal and digital signal.
In analog signal, 4mA corresponds to the minimum value of instrument signal. 20mA corresponds to the maximum value of instrument signal.
In digital signal, the device can send digital instructions to the instrument. The instrument can also send complete measurement data and fault diagnosis information.
Digital signals can be separated and analyzed through HART system, which improves the performance of the system and reduces the cost of field instruments.
Application examples of HART protocol

- Equipment adjustment: Through HART protocol, the parameters of field instruments can be adjusted remotely to achieve rapid adjustment of equipment.
- Fault detection and diagnosis: HART protocol allows equipment to obtain the measurement data and fault diagnosis information of the instrument, which helps to find and solve equipment faults in time.
- Valve control: According to the measurement data, the state of the inlet (outlet) valve can be controlled through HART protocol to achieve precise flow control.
If this article still can not explain the HART PROTOCOL for you, you can learn more about Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol
HART protocol specification
As an open, compatible, stable and reliable communication protocol, HART protocol has been widely recognized and applied in the industrial field.
After decades of continuous evolution, multiple versions have been updated and improved. Each revision brings new technologies and functions while being compatible with previous versions to meet the ever-changing development needs of industrial automation.
The main functions and differences of the current mainstream versions HART 5, HART 6 and HART 7 are as follows:
①Protocols before HART 5:
Physical layer: RS485;
Link layer: Token master-slave question and answer mode;
Application layer: define some simple general commands.
②HART 5 version protocol:
Physical layer: analog current + FSK, 1200bps;
Link layer: token master-slave question and answer mode, adding a second master device and a slave device burst mode;
Application layer: further enriches general commands, ordinary commands, special commands, and short address range 0 to 15.
③HART 6 version protocol:
Physical layer: Added current C8PSK, 9600bps specification;
Application layer: Expanded command content, used extended user identification, added device cluster command, short address range 0~63.
④HART 7 version protocol:
Physical layer: Added 2.4G DSSS O-QPSK 10dBm 250kbps specification;
Link layer: Added time division multiple access (TDMA) link control mode;
Network layer: Added self-organization, multipath, mesh network specifications;
Application layer: Expanded device cluster command, added mesh network maintenance command.
| Version | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Analog loop check | √ | √ | √ |
| Tag (8 characters) | √ | √ | √ |
| Device calibration | √ | √ | √ |
| Device configuration | √ | √ | √ |
| Broadcast message (burst) | √ | √ | √ |
| Multivariable communication (4) | √ | √ | √ |
| Primary variable with status | √ | √ | √ |
| Device status | √ | √ | √ |
| Long tag (32 characters) | √ | √ | |
| Locate device | √ | √ | |
| Digital loop check | √ | √ | |
| HART software lock | √ | √ | |
| Multivariable status | √ | √ | |
| Wireless | √ | ||
| Extended manufacturer ID | √ | ||
| Time stamp | √ | ||
| Trending | √ | ||
| Synchronous sampling | √ | ||
| Enhanced broadcast message – exception reporting | √ | ||
| Enhanced broadcast message – event notification | √ |
Featured HART Communicators and Smart Meters
hART protocol vs modbus
Modbus protocol and HART protocol are two different industrial communication protocols, which have the following differences:
Modbus protocol is a request/response protocol. That is, a master device can send request information or write data to multiple slave devices. The slave device will reply or execute only when it receives the request from the master device. HART protocol is a hybrid protocol that combines analog and data signals. That is, a digital signal is superimposed on the 4-20mA analog signal to achieve two-way data transmission and remote control.
Modbus protocol supports multiple physical layers and transmission modes, such as RS232/RS485/RS422, TCP/IP, wireless, etc. HART protocol mainly uses RS485 physical layer, and can also use wireless physical layer, but does not support TCP/IP transmission mode.
Modbus protocol can transmit multiple variables and information. The data type is limited and the number of nodes is limited. HART protocol can only transmit one primary variable and some secondary variables, device status and configuration data, with rich data types and unlimited number of nodes.
Modbus protocol is an open, compatible, flexible, easy-to-use protocol with no security guarantee. The HART protocol is an open, compatible, stable and reliable protocol with certain security guarantees.

More Measurement Solutions
- Pressure Transducer Wiring Diagram Guide: 2 Wire-3 Wire-4 Wire
- High Accuracy Pressure Transducers
- Flat Pressure Sensor for High Viscosity Fluids
- What Is Resistive Pressure Transducer?
- What Is a Fluid Pressure Sensor?
- What Is a Smart Pressure Transmitter?
- Industrial Slurry Density Measurement-Featured Slurry Density Meters
- Density 101: What Is the Unit of Measurement for Density
- Industrial Applications of Various Density Meters
- What Is Density Meter? and Types
HART is one of the most widely used bus protocols for industrial field devices. In addition, there are also common modbust protocols, Profibus protocols, FF Foundation bus protocols, etc.
Our simple introduction here cannot fully summarize such a protocol. There are still many details that are not included. For example, variable management, diagnostic definitions, etc. Please refer to the HART standard for specific development.
We Sino-Inst supply various process instruments with HART protocol. Including HART pressure transmitters, flow meters, level meters, etc. If you need to purchase, or have related technical questions, please feel free to contact our sales engineers!
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.








