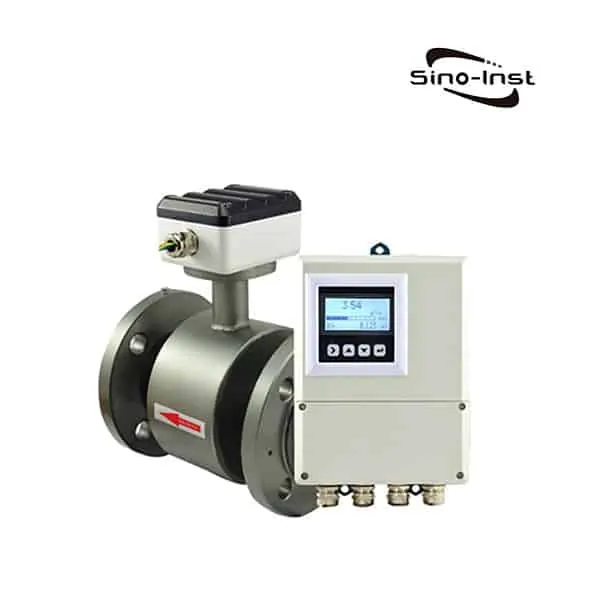
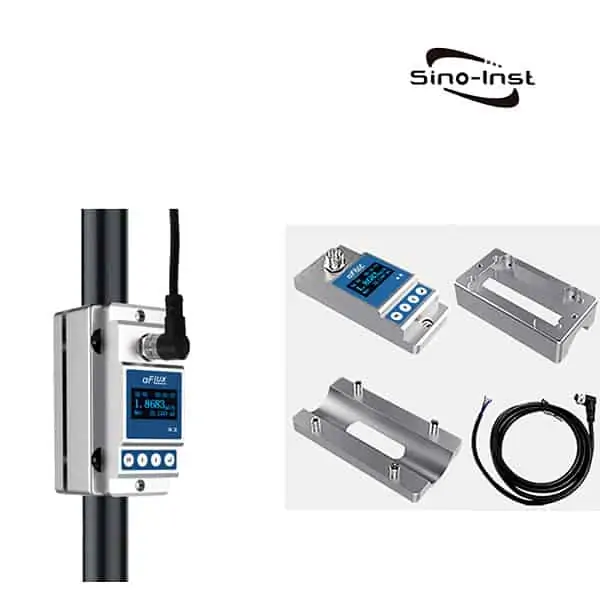
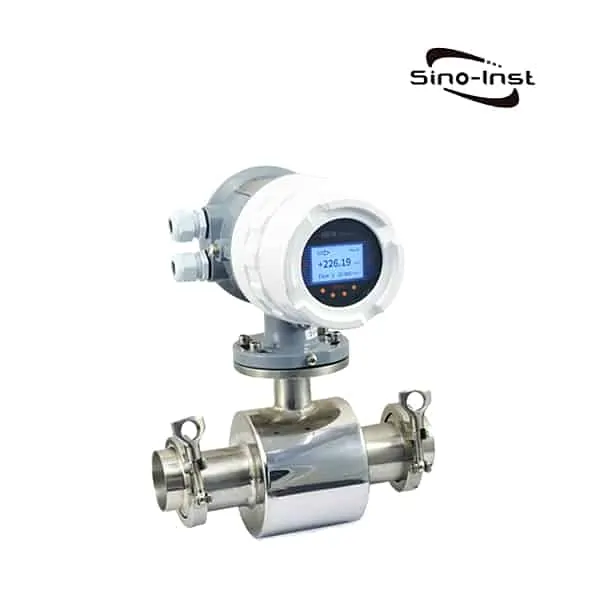
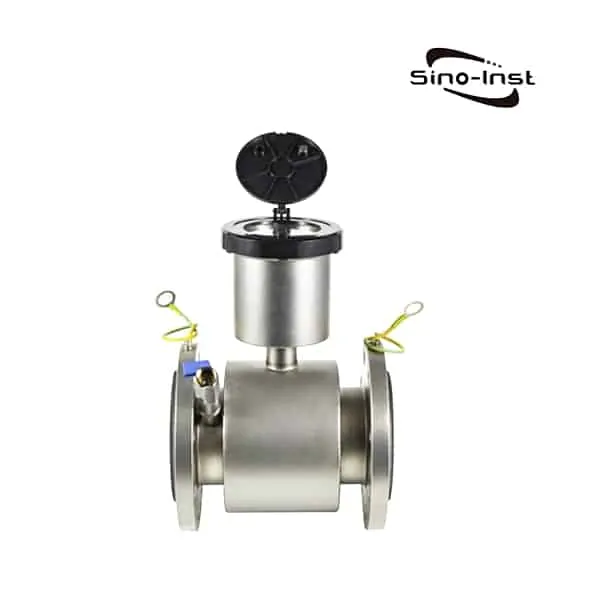
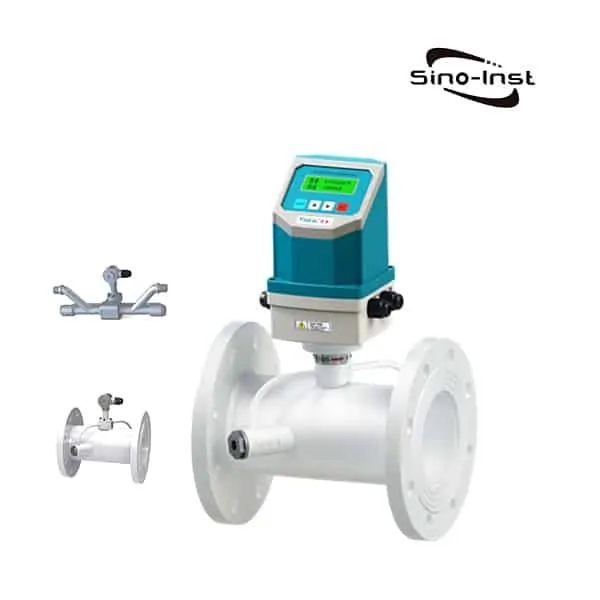
What is BTU Meter for Chilled Water?
The BTU Meter for Chilled Water accurately measures the thermal energy consumed by chilled water in British Thermal Units (BTU). This is a basic measure of thermal energy in commercial and residential buildings. BTU meters are used in chilled water systems in commercial, industrial and office buildings.
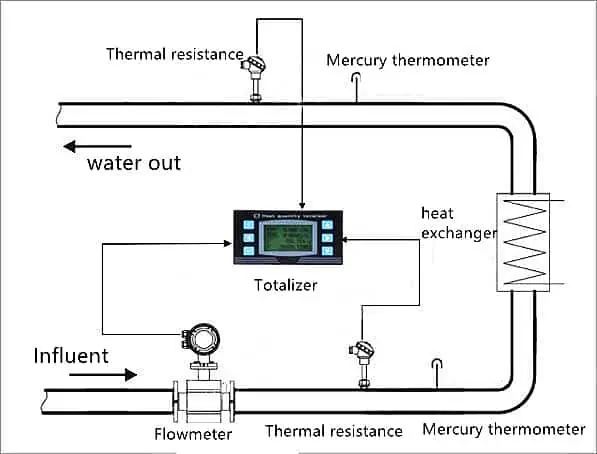
BTU Meter for Chilled Water is to install a pair of temperature sensors on the ascending pipe and descending pipe passing through the heat transfer fluid respectively. The flow meter is installed on the fluid inlet or return line. The integrator collects signals from flow and temperature sensors. Use the cumulative formula to calculate the amount of cold and heat obtained by the heat exchange system.
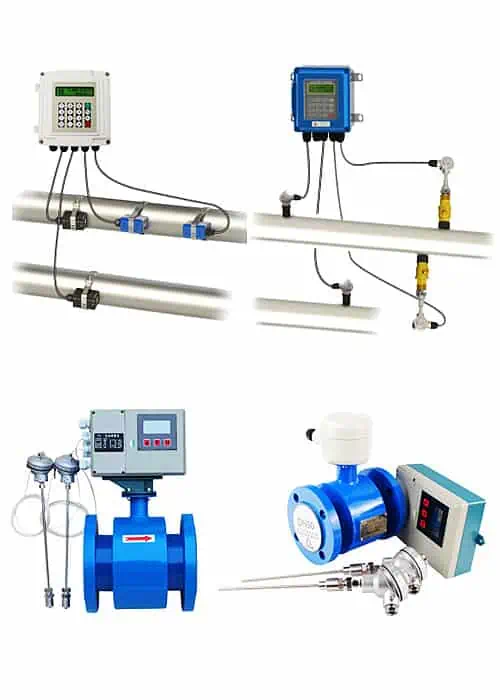

BTU Meter in Chilled Water System
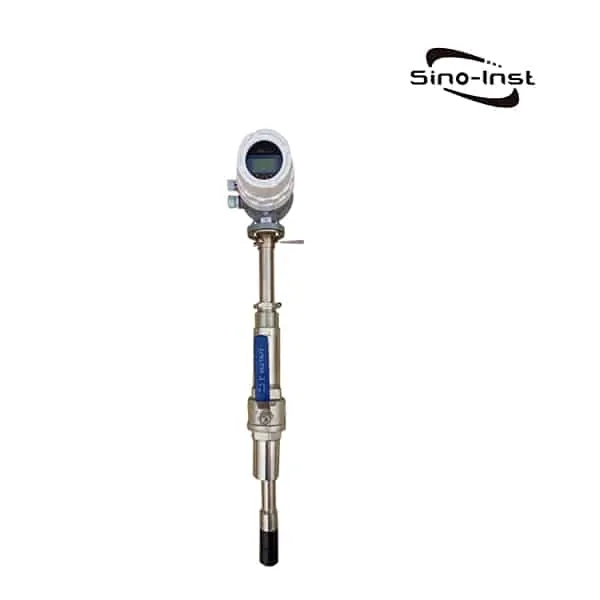
BTU Meter for Chilled Water consists of a flow measurement sensor, two temperature sensors and a microprocessor based energy calculator.
The flow sensor should be installed in the chilled water return line, and the chilled water flow direction should be installed in a vertical or horizontal position.
Two temperature sensors. A sensor is installed on the return line. The second sensor is installed on the water supply line.
The thermal energy transferred from the cooling water to the consumer over a defined period of time is proportional to the temperature difference between the flow and return flow and the amount of cooling water flowing through.
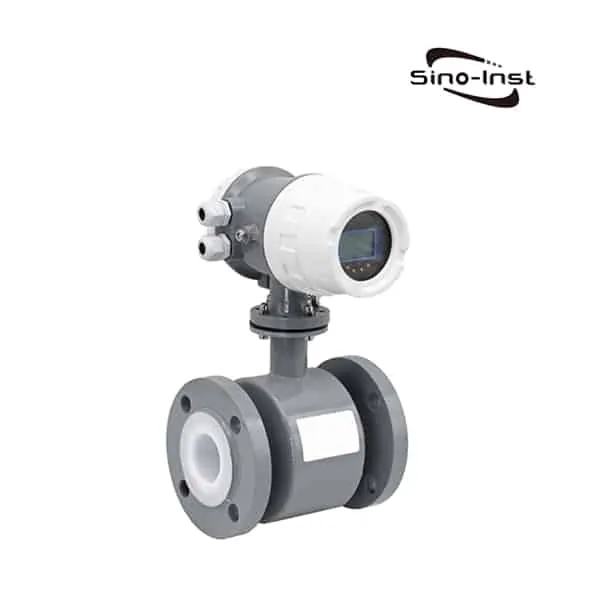
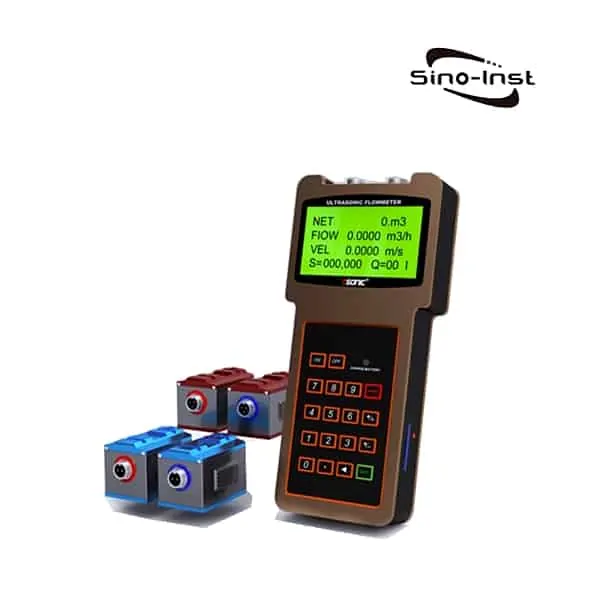
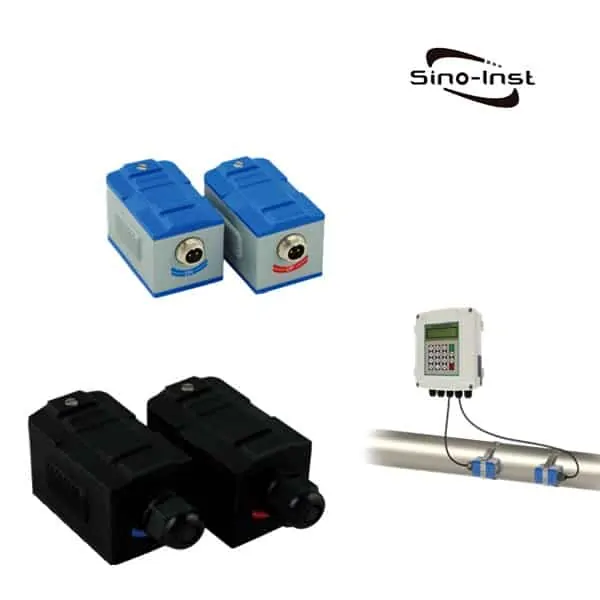
Sino-Inst offers two types of BTU Meter for Chilled Water. One uses ultrasonic measurement technology (ultrasonic BTU meter). Another uses the electromagnetic principle (electromagnetic cold and heat meter).
Extended Reading: 3 inch (3″) Water Flow Meter
BTU Meter Installation in Chilled Water System
With the increase of large buildings and modern buildings, the cooling system has developed rapidly. The demand for cooling capacity of industry and its chemical industry has also promoted the development of central cooling. Central cooling means that the power plant uses the cooling medium (usually fresh water and salt water) to supply the cooling capacity of the refrigerator to the user. In order to manage and account for the operation of refrigeration equipment. Settling the cooling energy consumed by the user. It is necessary to measure the cooling capacity of the relevant nodes.
The method of measuring the cooling capacity of chilled water is the same as that of hot water. The amount of cooling supplied can be seen as negative heat. Just due to the low temperature of the fluid. lead to some differences in specific practices.
Extended reading: Magnetic water meter-ultrasonic water meter-mechanical water meter
For chilled water used in air conditioners, the water temperature level is generally 5-6 °C. The cold medium is fresh water. For cooling below 5°C, use brine or other cooling media. The cold measurement method of fresh water chilled water mostly adopts the measurement method based on mass flow as shown in the figure below.
In the flow measurement of chilled water, the electromagnetic flowmeter has obvious advantages, and its characteristics are as follows:
- Magnetic flowmeter measurements are not affected by changes in fluid density, viscosity, temperature, pressure and conductivity.
- The electromagnetic flowmeter measuring tube has no obstructing flow parts, no pressure loss, and low requirements for straight pipe sections.
- The electromagnetic flowmeter sensor can be equipped with a ground electrode to achieve good grounding of the instrument.
- The electromagnetic flowmeter sensor adopts advanced processing technology, so that the instrument has a good ability to resist negative pressure.
In addition to the electromagnetic flowmeter measurement, the ultrasonic flowmeter can also be used for measurement. Customers can choose according to on-site conditions.
Extended reading: Dam water level measurement
BTU Meter Calculation
The BTU (British Thermal Unit) is universally accepted as a unit of heat transfer measurement. The BTU is defined as the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water 1°F. The equation for heat transfer to a liquid is as follows:
Q=W(T2-T1)Cp
Q=Heat transfer per unit time (BTU/hr)
W=Mass flow rate (lb/hr)
T2=Outlet temperature (°F)
T1= Inlet temperature (°F)
Cp=Specific heat capacity (1.0 BTU/lb for water)
Tools: BTU Calculator & BTU Formulas For Water Circulating Heat Transfer
BTU Meter vs Flow Meter
What is a BTU Meter?
BTU meters are flow meters with temperature sensors added to measure the energy consumption of any liquid heating or cooling system. BTU meters are also known as energy meters, heat meters. Commonly used are electromagnetic energy meters and ultrasonic energy meters. It is widely used in online metering of central air-conditioning cooling and heating energy metering and heating network. It can also be used to measure the performance of energy conservation measures or the loss of system efficiency that affects revenue. Read more about: What is BTU?
A flow meter (or flow sensor) is an instrument used to measure linear, nonlinear,mass or volumetric flow rate of a liquid or a gas.When choosing flow meters,one should consider such intangible factors as familiarity of plant personnel,their experience with calibration and maintenance, spare parts availability,and mean time between failure history, etc., at the particular plant site.
Extended reading: Ultrasonic water meter working principle
Frequently
Asked
Questions
Related Products
Related Blogs
Sino-Inst offers over 10 BTU Meter for Chilled Water. About 50% of these are magnetic flow meters, 40% is the ultrasonic flow sensor, and 20% are other flow meter.
A wide variety of BTU Meter for Chilled Water options are available to you, such as free samples, paid samples.
Sino-Instrument is a globally recognized supplier and manufacturer of flow measurement instrumentation, located in China.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.












