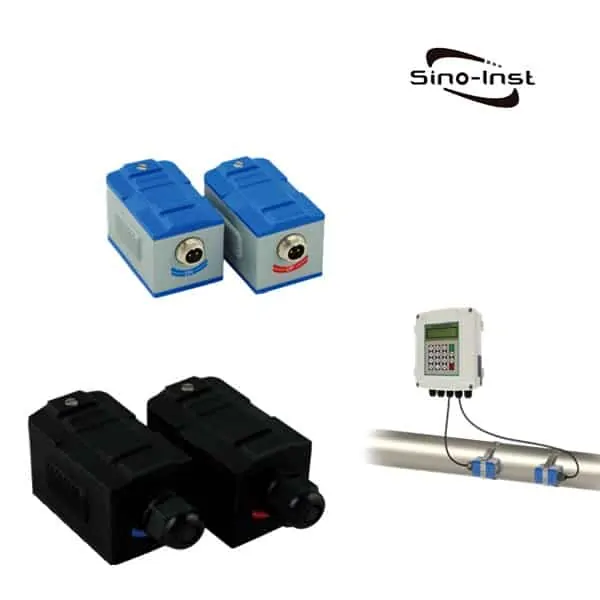
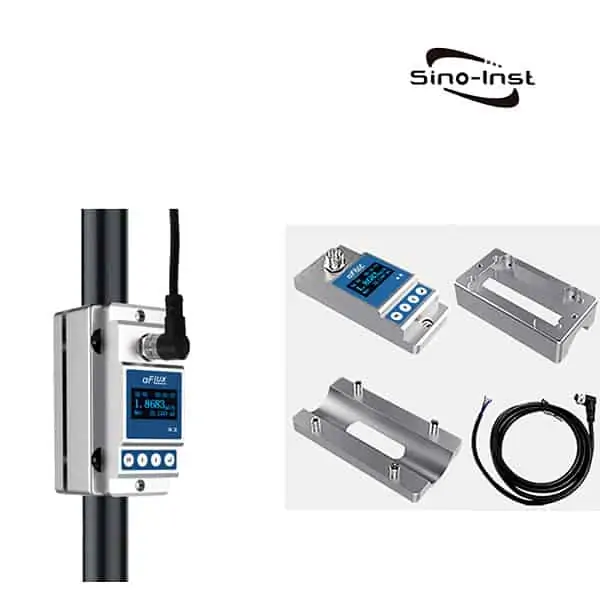
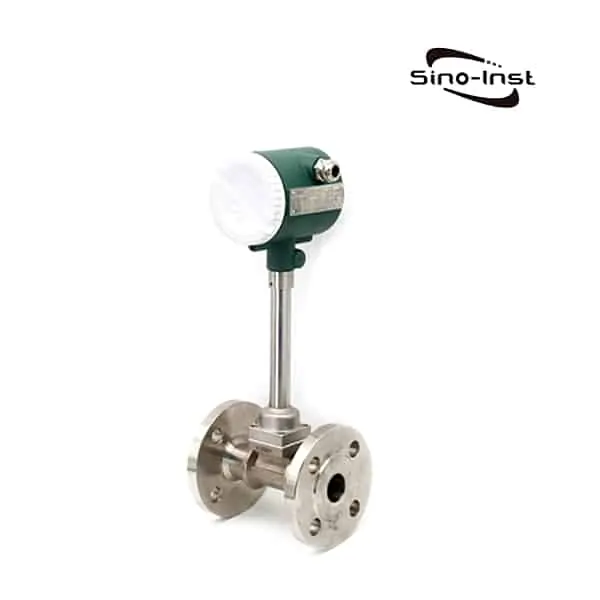
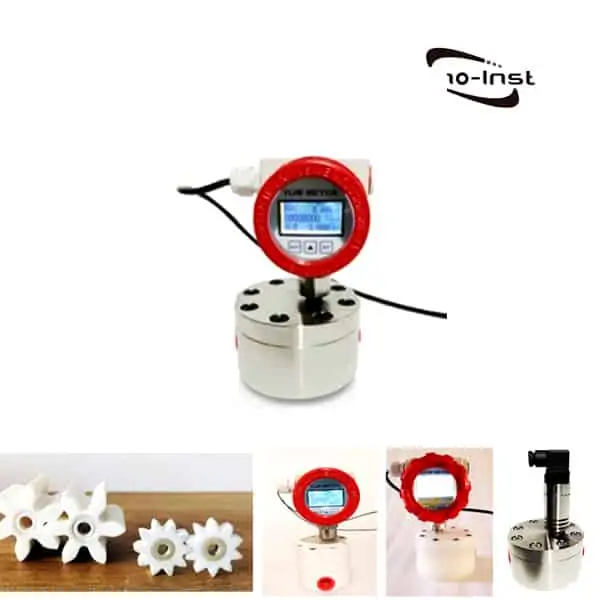
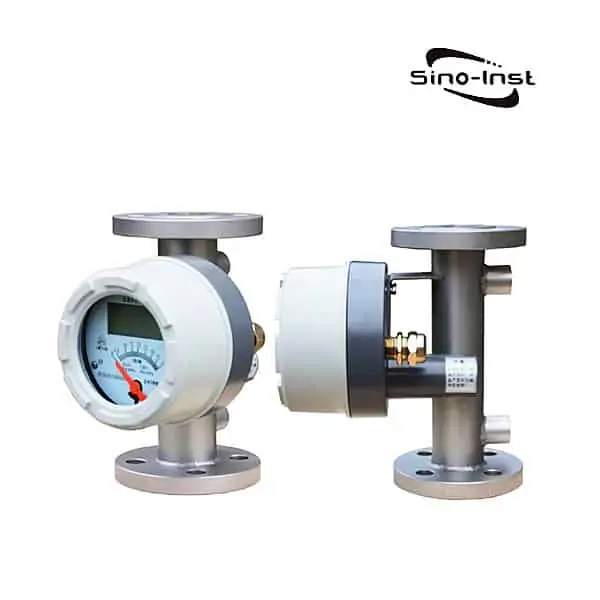
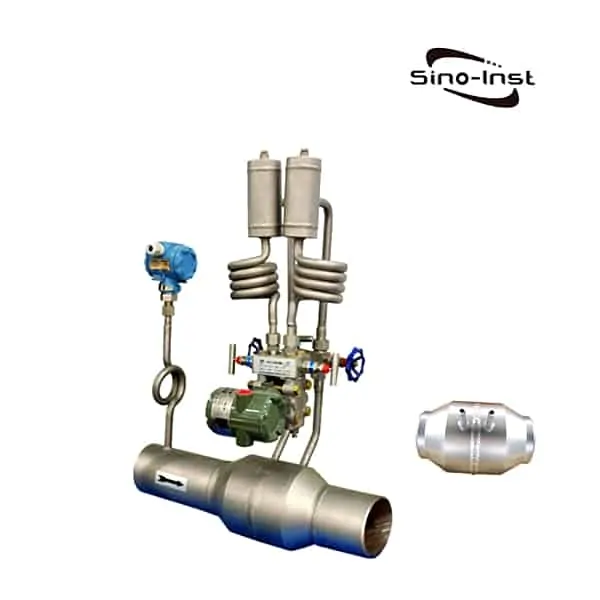
Condensate flow meters are essential tools designed to measure the flow of steam condensate in various systems and applications. The accurate measurement of condensate flow can eliminate blind spots in your plant and enable problem solving. These meters play a crucial role in managing energy consumption and optimizing system efficiency.

Importance of Measuring Condensate Flow
Measuring condensate flow is vital for several reasons.
First and foremost, it enables efficient energy management by monitoring the amount of energy being utilized in various processes.
Furthermore, measuring condensate flow is crucial for maintaining the safety and integrity of equipment, as it allows for early detection of issues such as leaks or blockages.
Lastly, monitoring condensate flow aids in regulatory compliance by adhering to environmental and industry-specific standards, promoting sustainable and responsible practices.
Technical difficulties in condensate flow measurement
Customers frequently need to measure the flow rate of condensate water returning from boiler systems or hot water pipelines. Such applications present unique characteristics:
- High water temperature: The flow meter sensor must be capable of withstanding temperatures around 150℃ (302℉).
- Low conductivity or demineralized water: Magnetic flow meters are unsuitable due to their requirement for conductive fluids.
- Pressure and Temperature Variations: Fluctuations in pressure and temperature can significantly impact the density and viscosity of the condensate, making it difficult to achieve consistent measurements.
- Installation Constraints: Proper installation is crucial for accurate flow measurement, but space limitations, pipe orientation, and varying pipe sizes can pose challenges.
- Scale and Corrosion: Over time, scale buildup and corrosion can impact the performance of flow meters.
- Fluid Properties: The properties of steam condensate, such as its conductivity, viscosity, and chemical composition, can impact the performance of certain flow meter technologies.

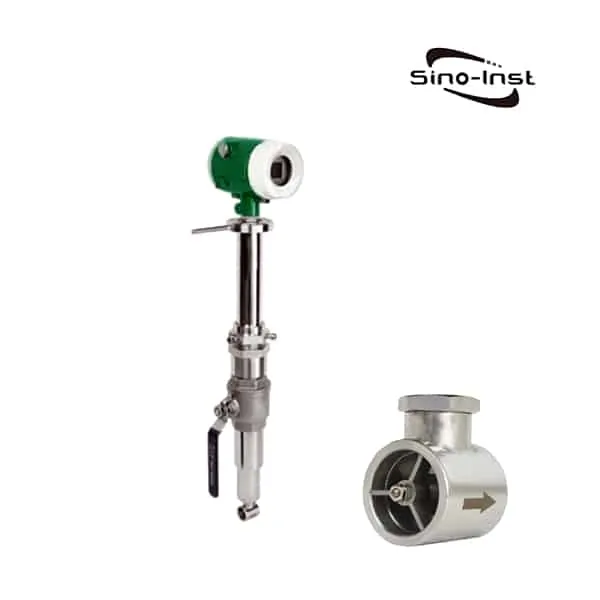
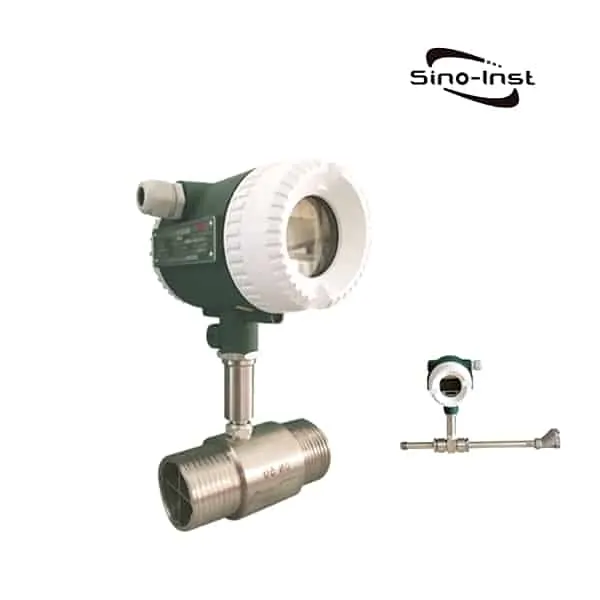
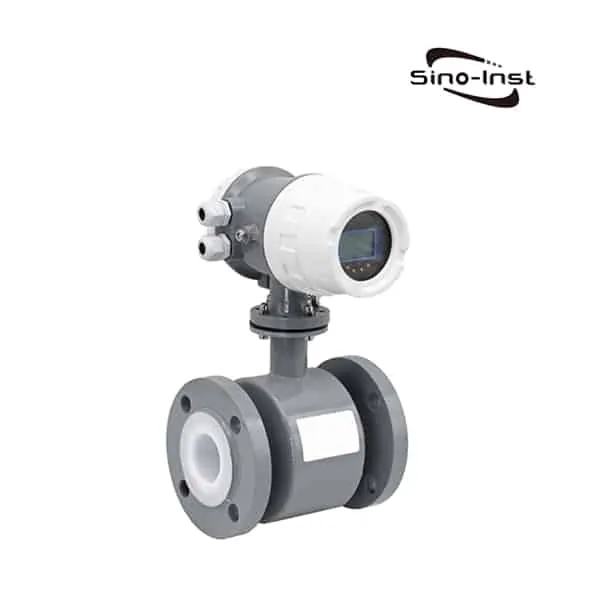
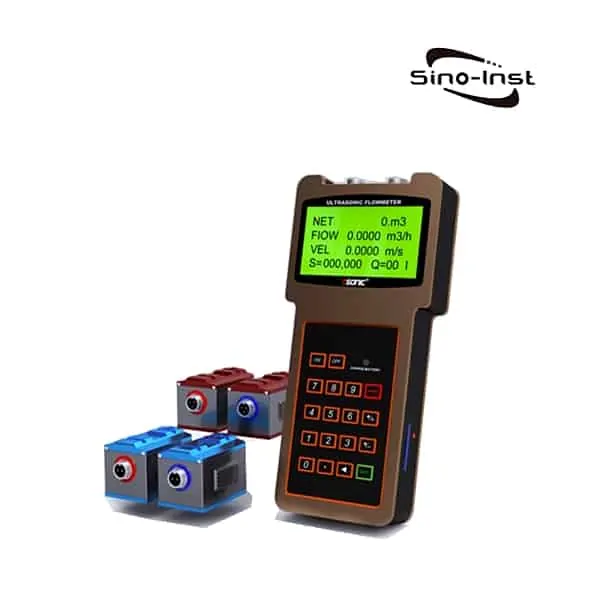
Types of Condensate Flow Meters
There are several types of condensate flow meters available, each with its unique working principle and suitability for specific applications. Some of the most common types include:
Each type of condensate flow meter has its advantages and limitations, so it is critical to select the right flow meter based on factors such as fluid properties, operating conditions, and application requirements.
Applications and Industries
Condensate flow meters find use in a wide range of applications and industries, some of which include:
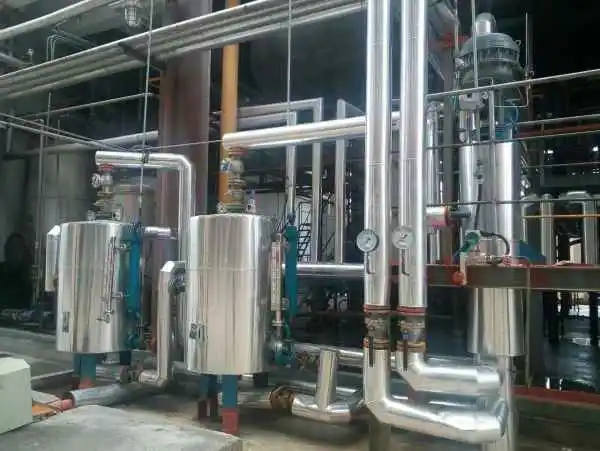

These are just a few examples of the diverse applications and industries that benefit from the accurate measurement and monitoring provided by condensate flow meters.
If you are working on the optimization of the above industry applications. Then it is very important to choose the right condensate flow meters or steam condensate flow meters.
Selection Guide
| Steps | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Understand your application | Identify specific requirements, including flow rate range, operating temperature and pressure, fluid properties, and accuracy needs. |
| 2. | Assess available technologies | Familiarize yourself with flow meter technologies (differential pressure, vortex, ultrasonic, turbine) and their suitability for steam condensate applications. |
| 3. | Condensate water flow meter functions | – Digital display to show instant flow and total flow – 4-20mA current output or pulse output – RS 485 Modbus RTU functions – Hart Protocol – Battery powered or 24V DC or 220V AC power supply |
| 4. | Evaluate installation constraints | Consider installation requirements, including straight pipe runs, mounting orientation, available space, and accessibility for maintenance. |
| 5. | Factor in maintenance and cost | Assess the total cost of ownership, including initial investment, installation, calibration, and maintenance expenses. Choose a cost-effective and easy-to-maintain flow meter. |
| 6. | Consult an expert | Reach out to a professional flow meter supplier or manufacturer with experience in steam condensate applications, such as Sino-Inst. Seek guidance and recommendations based on your needs and preferences. |
| 7. | Select and install the flow meter | Determine the most suitable condensate flow meter, and ensure proper installation and calibration according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable flow measurements. |
Frequently
Asked
Questions
More water and steam flow measurement solutions
Turbine Flow Meter Application Case: Demineralized Water
Measuring Oilfield Wastewater with Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Sea Water Flow Measurement – Magnetic vs Ultrasonic Flowmeters
BTU Meter for Chilled Water
Measuring Steam Flow and Steam Flow Meters
Steam Flow Measurement: Do you need temperature and pressure compensation?
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate condensate flow meter is crucial for efficient energy management, equipment safety, and process optimization across various industries.
With an array of options available, it is essential to consider factors such as fluid properties and operating conditions when making your choice.
As a professional supplier with extensive experience in steam condensate flow meters, Sino-Inst can help you find the right solution tailored to your specific needs.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to our experts for guidance and support in selecting the ideal flow meter for your application. Partner with us to ensure accurate and reliable steam condensate flow measurement in your operations.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.