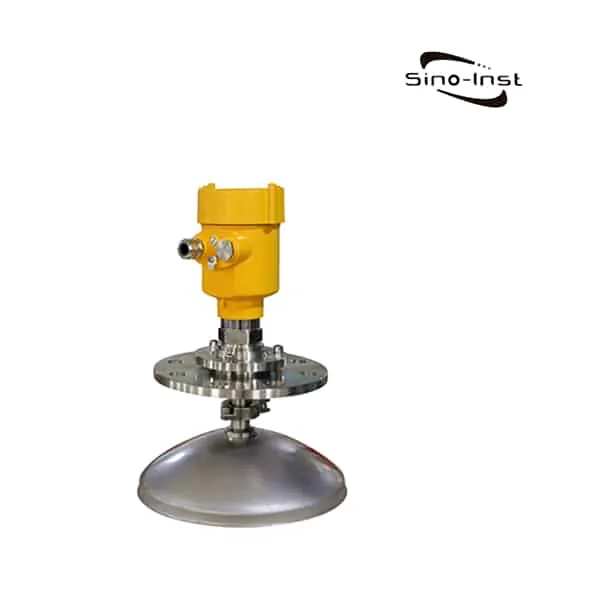
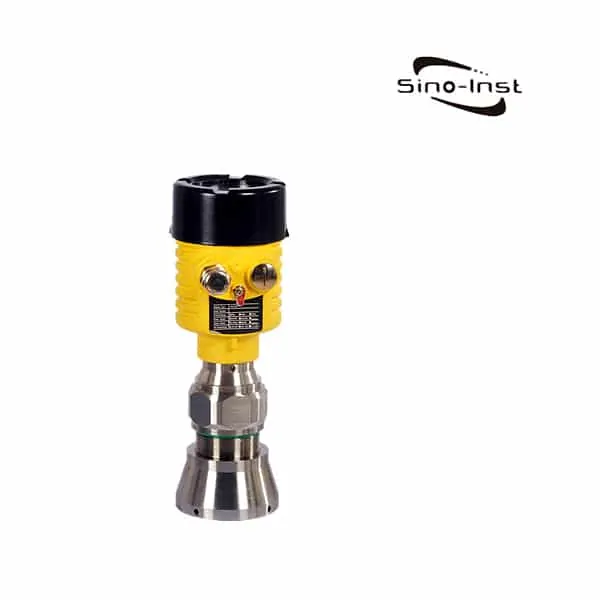
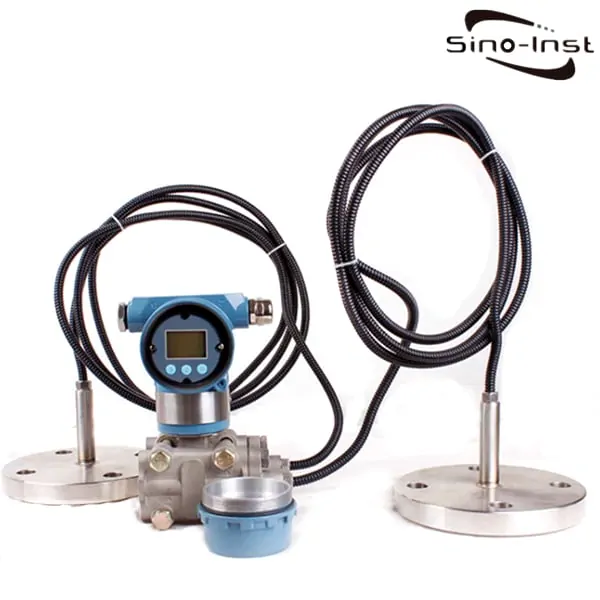
Guided wave radar level transmitter uses guided wave radar (GWR) technology. Based on the reflection of microwave on the surface medium. Through the probe, continuous level measurement of liquid and solid levels is completed.

A guided wave radar level transmitter is also called a wave-guided radar level sensor. They can measure both levels and the interface between two media. Through probe rod or cable, complete level contact types continuous level measurement. Such as Coaxial Probe Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitter. This is different from ultrasonic level measurement, which is non-contact measurement. A guided wave radar level transmitter is often used for tank level measurement. Including liquid and solid. Output 4~20mA/HART, so as to measure and control the level during production.
Sino-Inst offers a variety of Guided wave radar Level Transmitters for industrial level measurement. If you have any questions, please contact our sales engineers.
We also supply level transmitters, like: Pressure Level Transmitter; Submersible Level Transmitter; and (DP) level transmitter
Features of Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitters
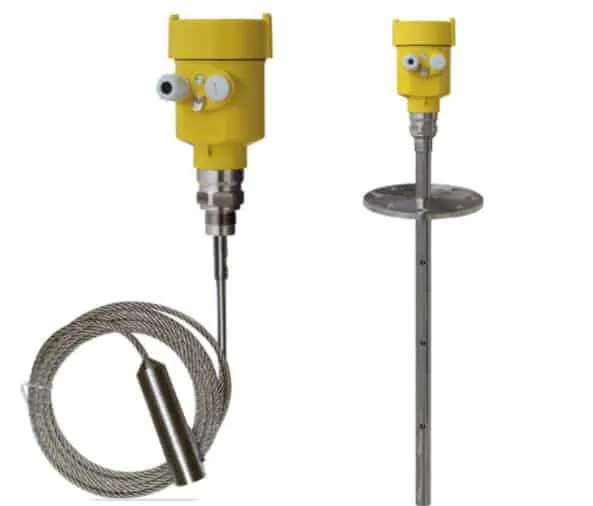

- Using advanced microprocessors and unique echoDiscovery echo processing technology, the guided wave radar level sensor can be used in a variety of complex conditions.
- A variety of process connections and types of detection components, guided wave radar level sensor for a variety of complex conditions and applications. Such as high temperature, high pressure, etc.
- With the pulse working mode, the guided wave radar level meter has very low transmitting power. And can be installed in various metal and non-metal containers without harm to the human body and the environment.
Customer benefits:
- Microwaves are unaffected by temperature, pressure, specific gravity and vapors
- Easy to install
- No moving parts
- Ignores light continuous coatings
- Good for vacuum service
- More direct energy return – more consistent signal
- Built-in waveform screen (Scope Trace)
Industries served:
- Oil and gas production
- Refining
- Pharmaceutical and biotech
- Power generation
- Pulp and paper
- Iron and steel
- Chemicals
- Food and beverage
- Marine
Parameters of SIRD70 Guided wave radar level transmitters
General Parameters
Probe Material:
- Rod Stainless Steel 316L/PTFE
- Cable Stainless Steel 316L/PTFE
- Coax Stainless Steel 316L/PTFE
- Seal Viton fluororubber , Kalrez Fluorinated rubber
- Process Connection Stainless Steel 316L
- Shell Stainless Steel 316L, Plastic,Aluminum
- Ground Terminal Stainless Steel 316L
Power: 2-Wire
- Standard Version (16~26)V DC
- Intrinsic Safe Version (21.6~26.4)V DC
- Power Consumption max. 22.5mA
- Ripple Allowed
- – <100Hz Uss < lV
- – (100~100K)Hz Uss < l0mV
Flameproof Type
- (22.8 ~ 26.4) V DC 2-wire system
- (198 ~242)V AC 4-wire system / 110V AC 4-wire system
- Power Consumption max. 1VA,1W
Output
- Output Signal (4~20)mA/HART
- Resolution 1.6μA
- Failure mode 20.5mA;22mA;3.9mA, hold
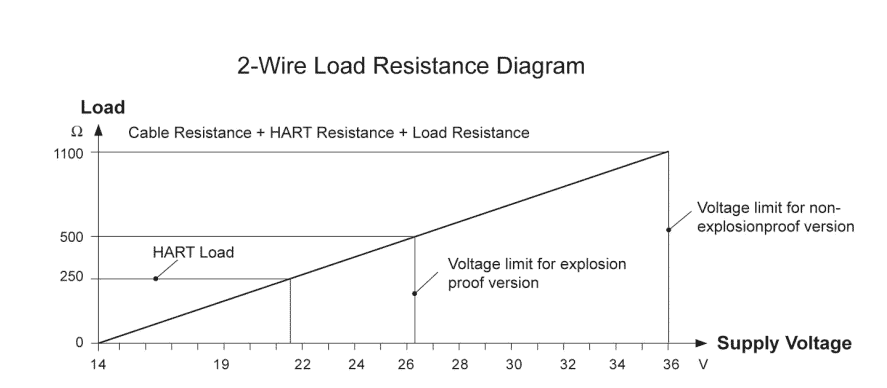
- 2-wire load resistance See the diagram below
- 4-wire load resistance Max.500 ohm
- Integration Time ( 0~36)sec, adjustable

Specifications of Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitters
| Max Measurement Distance | 701 30m/6m(Cable /Rod) 702 20m/6m(Cable /Rod) 703 30m/6m(Cable /Rod) 704 6 m 705 15m/6m(Cable /Rod) |
| Measurement Interval | About 1sec (Depend on parameter settings) |
| Adjustment Time | About 1sec (Depend on parameter settings) |
| Resolution of Display | 1mm |
| Accuracy | ±10mm(See the accuracy illustration diagram below) |
| Temperature for Storage/Transport (-40~80) ℃ | Process Temperature (Probe) 701、704 (-40~250)℃ 702 (-40~200)℃ 703 (-40~130)℃ 705 (-200~400)℃ |
| Relative Humidity | <95% |
| Pressure | Max. 40MPa |
| Vibration Proof | Mechanical vibration 10m/s² , (10~150)Hz |
guided wave radar level transmitter data sheet
Guided wave radar level transmitter range
Explanation:
H— Measuring range
L—Empty distance
B—The top of the blind
E—The minimum distance from the probe to the tank wall
–Blindspot is the minimum distance between the top of the highest material surface materials and the measurement reference point.
–The bottom of the blind refers to a distance near the very bottom of the cable that can not be accurately measured.
–Between the top and bottom of the blind is blind effective measure distances.
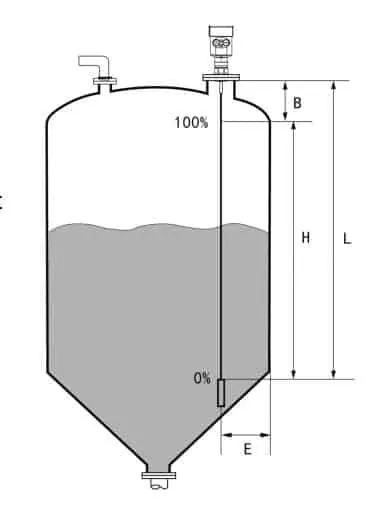
Note:
In order to ensure the accuracy of level measurement, the material should be located between the top and bottom of the blind.
Measuring Range:
The following table lists the relationship between different types of measured media and measurement distance.
| Media | DK(ε) | Solid particles | Liquid | Measuring range |
| 1 | 1.4~16 | – | -Condensation gas, such as N2CO2 | 3m (only refers to the coaxial rod probe) |
| 2 | 1.6~19 | -Plastic with particles -White limestone, special cement -sugar | -Liquefied petroleum gas, such as propane -Solvent -Freon 12/ Freon -Palm oil | 25m |
| 3 | 1.9~25 | -Ordinary cement, gypsum | -Mineral oil, fuel | 30m |
| 4 | 2.5~4 | -Cereals, seeds -stone -Sand | -Benzene, styrene, toluene -Furan -Naphthalene | 30m |
| 5 | 4~7 | -Wet stones, ores -salt | -Chlorobenzene, chloroform -Cellulose spray -Isocyanide hydrochloric acid, this amine | 30m |
| 6 | >7 | -mineral powder -Carbon black -coal | -Aqueous liquid -alcohol -Liquid ammonia | 30m |
Extended reading: Radar Level Meter for Corrosive Liquids
What is guided wave radar?

Micropower impulse radar (MIR) combines time domain reflectometry (TDR), equivalent time sampling (ETS), and modern low power circuitry.
This synthesis of technologies creates a high-speed Guided Wave Radar (GWR) transmitter.
The electromagnetic pulses are propagated via a waveguide, that focuses the energy and yields a system, many times more efficient than Non-Contact Radar (Non-contact radar level transmitters).
Time domain reflectometry (TDR)
TDR uses pulses of electromagnetic (EM) energy to measure distances or levels.
When a pulse reaches a dielectric discontinuity (such as one created by a media surface), a portion of the pulse is reflected.
The greater the dielectric difference between air and the process medium being measured, the greater the amplitude of the reflection.
Equivalent time sampling (ETS)
ETS, or Equivalent Time Sampling, is used to measure the high speed, low power EM energy.
ETS is a critical key in the application of TDR to vessel-level measurement technology.
The high-speed EM energy (1000 ft/us) is difficult to measure over short distances, and at the resolution required in the process industry.
ETS captures the EM signals in real time (nanoseconds), and reconstructs them in equivalent time (milliseconds), which is much easier to measure with today’s technology.
Guided-wave radar (GWR) level transmitter working principle
Levelflex works with high-frequency radar pulses, which are emitted and guided along with the probe.
As the pulse meets the medium surface, part of the emitted pulse is reflected due to a change of the dc value (relative dielectric constant).
The Time-of-Flight between pulse launching and receiving is measured, and analyzed by the instrument and constitutes a direct measure for the distance, between the process connection and the product surface.
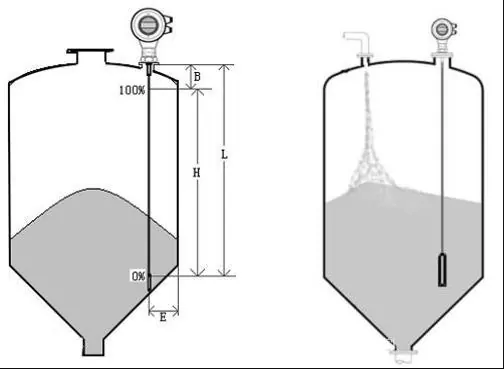
What is the difference between radar and ultrasonic level transmitter?
Radar liquid level sensors and ultrasonic liquid level sensors are non-contact liquid level measuring instruments. They mainly differ in the following three aspects:
Working principle
- Ultrasonic level sensor
The ultrasonic level sensor uses non-touch measurement method. It is suitable for liquid level measurement in water conservancy and hydrology, chemical petroleum and sewage treatment. The probe of the ultrasonic level sensor is also called a transducer. The transducer emits ultrasonic pulses to the object to be measured. After touching the surface of the medium, the sound wave is reflected by the surface of the medium and is received by the transducer again. The time from when the sound wave is emitted to when it is absorbed and consumed after reflection will be proportional to the distance between the transducer and the medium. - Radar level sensor
Radar level sensors also use non-touch measurement methods. The measuring principle is similar to that of an ultrasonic level sensor. That is, the antenna emits electromagnetic waves, and the electromagnetic waves are reflected back after reaching the measured liquid surface. Then the antenna receives and recognizes the time distance that Baud has.
Adaptability
The time consumed by the ultrasonic storage and analysis of the sound waves in each period of the ultrasonic level sensor is slightly longer. For this reason, if the rate of liquid level change is too fast, it is generally not recommended to use an ultrasonic level sensor. In addition, the ultrasonic level sensor is sensitive to misty vapor and fine dust within the area. Therefore, ultrasonic level sensors are not suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments, misty spaces filled with vapor, or spaces with dust. But on the contrary, the radar level sensor can prevent the disturbance of the above-mentioned environment.
Cost performance
The market price of ultrasonic level sensors produced in China usually ranges from one thousand yuan to several thousand yuan. The appearance of its products is more delicate than that of radar level sensors, so transportation costs will be reduced accordingly. In comparison, the structural design of the radar level sensor is more messy and the measurement steps are more refined, so the price is higher. Especially when the user needs a radar level sensor with HART protocol, the unit price is more expensive. But now the price gap is not big, and it is shrinking year by year.
Through induction and comparison, it is not difficult to find that the ultrasonic level sensor and the radar level sensor have their own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, it is recommended that users should consider many aspects when purchasing liquid level timing. It is not only necessary to meet the preset specifications, but also to scientifically include the above aspects into consideration.
Extended reading: Ultrasonic Oil Level Sensor-External Paste-Truck Fuel Tank
Maybe you still have questions like:
How to calibrate radar level transmitter?
What’s the guided wave radar level transmitter principle of operation?
You can just contact us for more information about GWR level transmitters.
Our guided wave radar (GWR) level transmitters, are made in China,
With better price, and higher quality.
Frequently
Asked
Questions
Related Products
Related Blogs
Sino-Inst offers over 10 GWR Corrosive Liquid Chemical Level Sensors for level measurement. About 50% of these are Guided Radar level meters, 40% is the tank level sensor.
A wide variety of GWR Corrosive Liquid Chemical Level Sensors options are available to you, such as free samples, paid samples.
Sino-Inst is a globally recognized supplier and manufacturer of Guided Wave radar level measurement instrumentation, located in China.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.

















