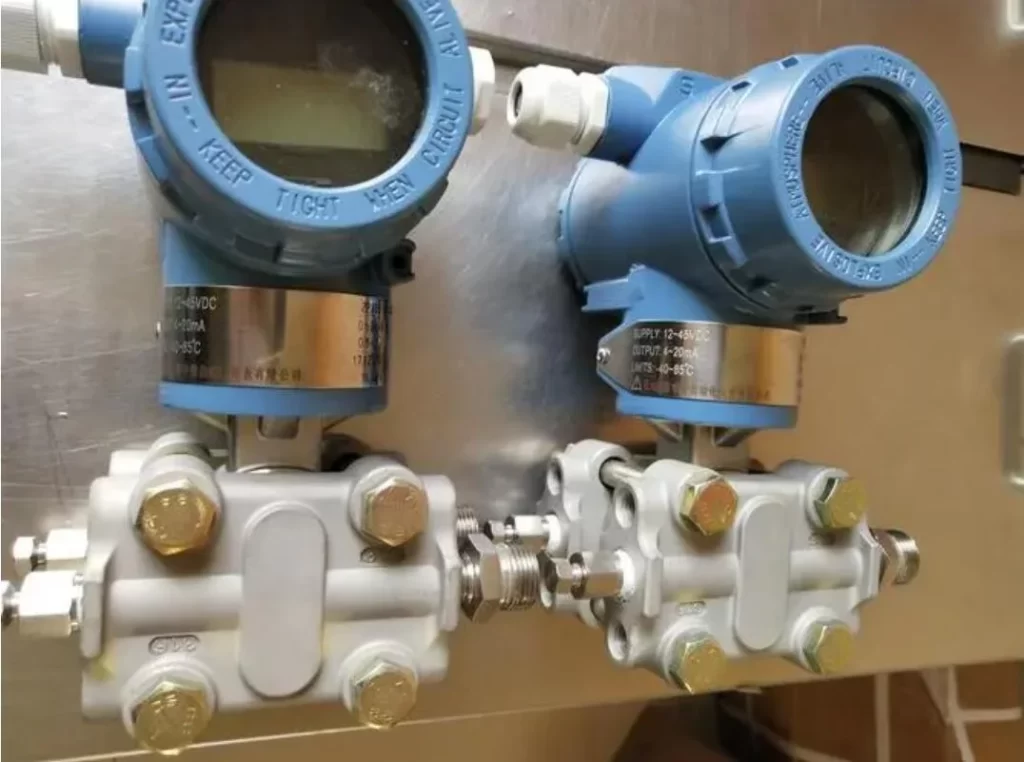
Pressure transmitter calibration is what you need to do before you install the pressure transmitters. Also called pressure transducer calibration, or pressure sensor calibration.
In this article, we will share pressure transmitter calibration using hart communicator.
Pressure transmitters used in the process industries are very durable and reliable instruments.
Even so, they still require periodic maintenance and calibration to ensure optimal performance.

Before we start to calibrate the pressure transmitter, we should know:
What is span in pressure transmitter?

Fig. showing span and zero adjustment
Span value:
The difference between two minimum value and maximum value of readings is known as a span value.
As shown in fig. below span = 20mA – 4mA
Zero Value:
The value of readings at zero lines (Y-axis) is known as zero value as shown in the figure.
How Often Should You Calibrate a Pressure Transmitter?
Pressure transmitters require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure optimum performance.
There are no specific rules for the calibration of pressure transmitters. However, this depends on the regulations the company must comply with and the purpose of the calibration. Examples include safety specifications, application requirements, process conditions or as part of standard maintenance.
General industry practice is to calibrate pressure transmitters every 1 to 3 years based on the above conditions.
If it is found that there are obvious errors, or it is more important, the calibration cycle can be shortened.
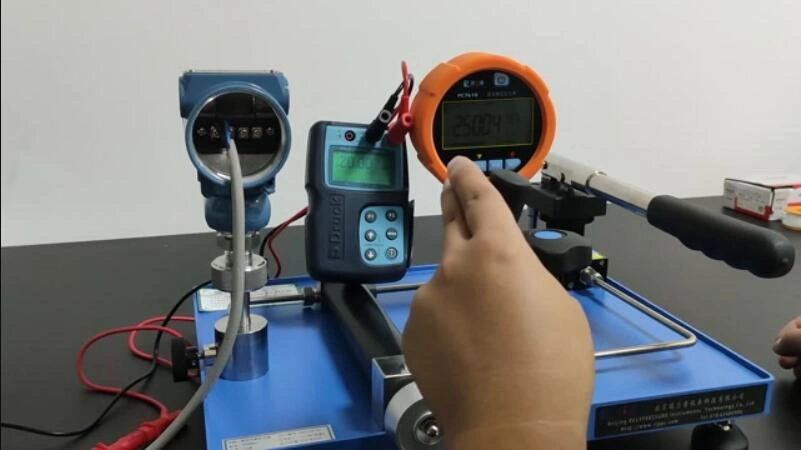

Extended reading: Pressure Sensor Applications-Featured Industry Applications
how to calibrate a 4-20mA pressure transmitter
Once you have established the calibration interval and MPE, you are ready to perform the actual calibration procedure on your pressure transmitter.
The best-practice recommendation is:
-
Mount the transmitter in a stable fixture free from vibration or movement.
-
Exercise the sensor or membrane before performing the calibration.
This means applying pressure and raising the level to approximately 90 percent of the maximum range.
For a 150 psi cell that means pressurizing it to 130–135 psig. Hold this pressure for 30 seconds, and then vent.
Your overall results will be much better than if you calibrate “cold.” cent of the maximum range.
For a 150 psi cell that means pressurizing it to 130–135 psig.
Hold this pressure for 30 seconds, and then vent.
Your overall results will be much better than if you calibrate “cold.” -
Perform a position zero adjustment (zero the transmitter).
This is important because the orientation of the fixture used for calibration may be different than the way the transmitter is mounted in the process.
Failing to correct for this by skipping this step can result in nonconformance.
You may like:
Magnetostrictive level transmitters
Magnetostrictive level sensor -
Begin the Pressure Transmitter Calibration procedure.
Typically this means three points up (0 percent/50 percent/100 percent) and then three points down.
The 4–20 mA output should be 4 mA, 12 mA, and 20 mA at the three points (or the correct digital values for a smart transmitter).
Each test point should be held and allowed to stabilize before proceeding to the next.
Normally that should take no more than 30 seconds.
You can use more points if you require higher confidence in the performance of the instrument. -
Compare the results of your pressure transmitter to your reference device.
-
Document the results for your records.
Pressure transmitter calibration formula
There is a formula that we can easily use to convert most (or all) units utilizing 4 to 20 mA signal to mA units.
There are others out there but this is the simplest I know.
Below is a simple formula for pressure to current conversion.

For example:
the range is : 0 to 10 Bar
Full range = 10 Bar
Displayed or measured value: 7 Bar
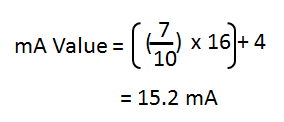
15.2 mA is the equivalent current value of a 7 Bar pressure.
(Read more about: Common Units Of Pressure)
For Value or range which is not starting with zero ( with a vacuum range), use below linear interpolation formula.
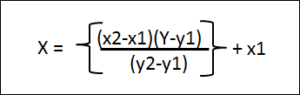
You can also encode this to excel for easier conversion.
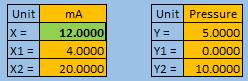
If you want to know and calculate the error,
Just subtract the True value with your computed value.
Error = Measured Value – True Value.
If the Pressure Transmitter has an accuracy of 0.5% of the range,
then 0.005 x 7= +/-0.035 Bar,
you can use this as the tolerance to determine a pass or fail result.
Or you can ask the user for their respective tolerances.
Read more about: What Is 0-10V Signal Output?
How to calibrate pressure transmitter with hart communicator
Equipment required for Pressure Transmitter Calibration
Pressure transmitter, multimeter, HART communicator
The basic procedure for Pressure Transmitter Calibration
- Isolate the Pressure Transmitter from the Process.
- Slowly open the vent plug and the vent valve to release the pressure.
- Connect the multimeter with the transmitter and ensure that output is 4ma when 0 pressures are applied.
- Connect the handheld test pump (pressure source) to the transmitter.
- Ensure there is no leak.
- Apply pressure range at 0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, 100% and check there is any error.
- If there is any error calibration should be done.
Read more about HART Pressure Transmitter
If the transmitter is the analog transmitter
- Apply 0% pressure as per LRV with handheld test pump and check multimeter if it is not 4ma adjust the zero pot in the transmitter and correct transmitter output to 4ma
- Apply 100%pressure as per the URV and correct 20ma in multimeter by adjusting span pot in the transmitter
- Repeat these steps to rectify the error.
In case of SMART Transmitter
- We have to use HART communicator, connect the communicator with the transmitter select the HART Communicator Menu for lower range value trim and upper range value trim.
- Basic Set up – Calibration – Zero Trim/Sensor Trim —Lower/Upper range value trims.
- HART communicator will automatically calibrate the transmitter.
- Restore the process connection
- Take the transmitter on line. Ensure there is no leak
a small example of five-point calibration is given below
Low range value=0psi
upper range value=200psi
This calibration can work for Rosemount 3051 calibration.
Learn more about Pressure Transmitter Calibration
If you cannot find an answer to your question in our Pressure Transmitter Calibration you can always contact us and we will be with you shortly.
More Pressure Measurement Solutions
Conclusion:
It is normal for the pressure transmitter to have a certain error. But if the error is too large, it needs to be calibrated. There are two types of Pressure Transmitter Calibrations: conventional method and intelligent calibration. no matter where
Kinds of preparations must be done before calibration, and then calibrate and debug through the handheld operator.
There are no mandatory fixed requirements for Pressure Transmitter Calibration. Generally, enterprises can formulate them by themselves. Normally, they can be calibrated once a year. Crucially, the calibration cycle can be shortened.
About how to calibrate the pressure transmitter, and what needs to be paid attention to during the process of Pressure Transmitter Calibration. If you still have questions, please feel free to contact our engineers.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.