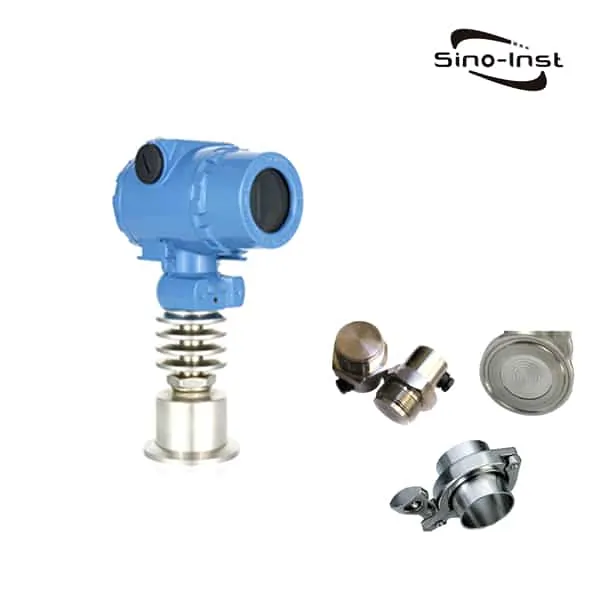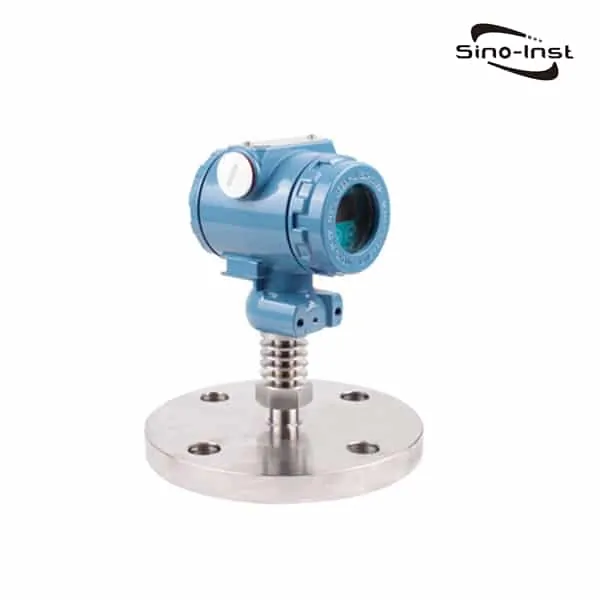
What is a gauge pressure transmitter?
Gauge Pressure Transmitter/Transducer is a commonly used pressure measurement process instrument in industry. The gauge pressure transmitter measures the pressure signal at the reference end of atmospheric pressure.
An industrial gauge pressure transmitter is commonly used to monitor the process pressure of liquid, gas, steam, etc.
Sino-Inst offers a variety of Gauge pressure transmitters for industrial pressure measurement. If you have any questions, please contact our sales engineers.
Benefits of Gauge Pressure Transmitter

- High accuracy: The pressure transmitter can perform high-accuracy measurements within the measurement range of 0~60MPa.
- Excellent overpressure performance: Can withstand 2 times the pressure range.
- Intelligent static pressure compensation and temperature compensation protect the transmitter from the influence of temperature, static pressure and overpressure, reducing errors.
- LCD digital display with backlight
- Built-in three-button quick operation and local adjustment function
- Various anti-corrosion materials are available
- Multi-faceted self-diagnosis function
- Optional signals 0-10V, 4-20mA, RS485, HART protocol, etc.
Read more about: Common Units Of Pressure
Specifications of Gauge Pressure Transmitter
| Use object: | Liquid, gas or steam |
| Measuring range | 0-3.5~35kPa 0-10~100kPa 0-35~350kPa 0-0.1~1.0MPa 0-0.35~3.5MPa 0-1.0~10MPa 0-2.1~21MPa 0- 4.1~41Mpa 0- 6.0~60MPa |
| Output signal: | 4-20mAdc. Output, superimposed HART protocol digital signal (two-wire system) |
| Power source: | External power supply 24V dc. Power supply range 12V ~ 45V |
| Installation in dangerous places | Flameproof ExdIIBT5Gb; (explosion-proof certificate no. :CE16.1163) Intrinsically safe ExiaIICT4/T5/T6Ga; (explosion-proof certificate no. : CE15.2354X) |
| Accuracy: | ±0.1%, ±0.075% |
| Stability: | ±0.2%/12 months of the maximum range |
| Temperature effect: | Including zero and range for maximum temperature error of ±0.2% / 20 ℃ |
| Power supply impact: | Less than 0.005% / V of the output range. |
| Vibration effect: | In any axial direction, the frequency is 200Hz, and the error is ±0.05% / g of the maximum range. |
| Electronic circuit board work in: | – 40 ~ 85 ℃; |
| Sensitive components work in : | – 40 ~ 85 ℃; |
| Storage temperature : | – 40 ~ 85 ℃; |
| With digital display: | – 25 ~ 75 ℃ (run); – 40 ~ 85 ℃ (no damage); |
| Relative humidity: | 0 ~ 95% |
| Overpressure limit: | 2~5 times the maximum range of the pressure transmitter is not damaged. |
| Volume change: | Less than 0.16cm3 |
| Damping: | The time constant is adjustable from 0.1 to 32.0s. |
| Startup time: | 3s, no preheating required. |
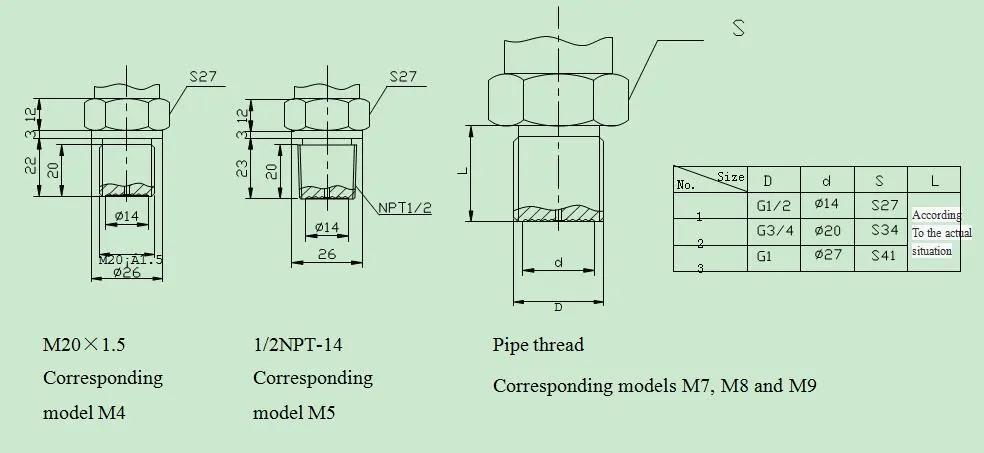
Extended reading: How to calibrate HART pressure transmitters
Common Industrial Applications of Gauge Pressure Transmitter
Gauge pressure transmitter is the most commonly used detection instrument in industrial process control, which is widely used in various automatic control systems. Such as aerospace, military industry, petrochemical, chemical industry, oil well, electricity, shipbuilding, building materials, pipelines and many other industries.
It is generally used to measure pressure or absolute pressure in environments where the medium temperature is not too high, the corrosiveness is not strong, the viscosity is not high, and it is not easy to crystallize.
If low temperature, high temperature, corrosive medium measurement is required. Please contact our engineers for customization!
- Mechanical and plant engineering
- Chemical industry
- Medical technology
- Food and beverage
- Oil and gas industry
- Packaging and paper industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
Read more about: What is industrial pressure transmitter?
Explosion Proof Pressure Transmitter for Hazardous locations
Gauge pressure transmitter working principle
SMT3151 TGP-Gauge Pressure Transmitter / Transducer is a diffusion silicon pressure transmitter. The working principle of the diffused silicon pressure sensor is based on the piezoresistive effect.
Using the principle of piezoresistive effect, the pressure of the measured medium directly acts on the diaphragm of the sensor (stainless steel or ceramic).
Make the diaphragm produce a slight displacement proportional to the pressure of the medium. To change the resistance value of the sensor. Use electronic circuits to detect this change. And convert and output a standard measurement signal corresponding to this pressure.
More about : Pressure transmitter Working Principle.
Difference between absolute, gauge, and differential pressure
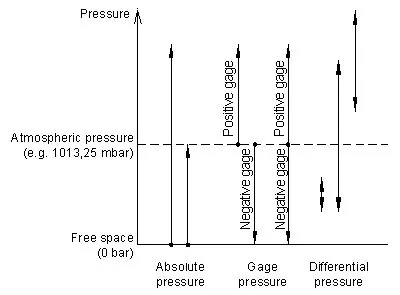
Absolute pressure
Absolute pressure is referred to as the vacuum of free space (zero pressure). In practice, absolute piezoresistive pressure sensors, measure the pressure relative to a high vacuum reference, sealed behind its sensing diaphragm.
The vacuum has to be negligible compared to the pressure to be measured. Sino-Instrument’s absolute pressure sensors, offer ranges from 1 bar or even 700 mbar as well as barometric pressure ranges.
Gauge pressure
Gauge pressure is measured relative to the ambient atmospheric. The average atmospheric at sea level is 1013.25 mbar. Changes of the atmospheric, due to weather conditions, or altitude influences the output of a gauge pressure sensor.
A gauge pressure higher than ambient pressure is referred to as positive pressure. If the measured pressure is below atmospheric, it is called negative or vacuum gauge pressure. In general, a vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter.
According to its quality vacuum is divided into different ranges such as an e.g. low, high and ultra high vacuum.
Differential pressure
Differential pressure is the difference between any two process pressures p1 and p2. Differential pressure sensors must offer two separate pressure ports, with a tube or thread. Sino-Instrument’s amplified pressure sensors, are able to measure positive and negative pressure differences. i.e. p1>p2 and p1<p2.
These sensors are called bidirectional differential pressure sensors, with ranges of e.g. -1…+1.0 bar or -2.5…+2.5 mbar. In contrast, unidirectional differential pressure sensor only operate in the positive range (p1>p2). E.g. from 0…1.0 bar or 0…2.5 mbar. And the higher has to be applied to the pressure port defined as “high pressure”.
Gauge Pressure VS Absolute Pressure
- Gauge pressure refers to pipeline pressure. It refers to the pressure measured with pressure gauges, vacuum gauges, U-shaped tubes and other instruments, also called relative pressure). “Gauge pressure” starts from atmospheric pressure.
- The pressure directly acting on the surface of the container or object is called “absolute pressure”. The absolute pressure value starts with absolute vacuum.
Absolute pressure actually refers to the gauge pressure plus the local atmospheric pressure (generally a standard atmospheric pressure can be 101.3Kpa).
Absolute pressure = gauge pressure + one atmosphere
If the unit is MPa, absolute pressure = gauge pressure + 0.1MPa
Read more about: Absolute Pressure Vs Gauge Pressure Measuring Instruments
More Featured Pressure Transmitters and Pressure Measurement Solutions
- Static Pressure vs Dynamic Pressure vs Total Pressure
- Introduction to Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
- What Is an Air Pressure Transducer?
- Steam Pressure Transmitter
- Cryogenic Pressure Transducers
- High Frequency Dynamic Pressure Sensor
- Intrinsically Safe vs Explosion Proof Pressure Transmitters
- How to Calibrate a Pressure Transmitter
We at Sino-Inst manufacture and supply various types of gauge pressure transmitters for various industries. Customized production is available based on your measurement requirements, including pressure range, temperature, accuracy, signal output, mounting thread, material, etc.
If you need to purchase a gauge pressure transmitter, or have any technical questions, please feel free to contact us.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.








