Imagine being in a world where pressure measurements are a hassle. You’re constantly struggling with inaccurate readings, device malfunctions, and complicated setup processes. Sounds exhausting, right? Now enter voltage pressure transducers. These little devices are the unsung heroes of the industrial world, transforming your pressure measurement process from a frustrating chore into a smooth, reliable operation. Let’s dive in and learn more about these game-changing tools.
What is a Voltage Pressure Transducer?
A voltage pressure transducer is an electromechanical device that converts pressure into an analog voltage signal. This signal can be easily read and analyzed, making pressure monitoring a breeze. But how does it all work? Let’s find out.
More detailed guide about pressure transducers here:
- 0-5 Volt Pressure Transducers
- What Is Hydrostatic Pressure?
- What Is the Difference Between Class 1 Div 1 and Class 1 Div 2 ?
- 0-10v Pressure Transducers | 3 or 4 Wire Configuration
- Different Types of Pressure: Absolute, Gauge, Sealed Gauge and Differential Pressure
- Pressure Transducer Wiring: 2 Wire-3 Wire-4 Wire
- High Temperature Pressure Transducer with Best Price
- How to convert a 4-20mA to 0-10V /1-5V signal?
- Differences! Static Pressure vs Dynamic Pressure vs Total Pressure
- Introduction to Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
- What Is an Air Pressure Transducer?
- Steam Pressure Transmitter
- Cryogenic Pressure Transducers
- High Frequency Dynamic Pressure Sensor
- How Does a Pressure Transmitter Work?
- Pressure Transmitter Calibration
The Inner Workings of Voltage Pressure Transducers
At the heart of every voltage pressure transducer is a sensing element, often a strain gauge or a piezoresistive sensor. When pressure is applied, this element deforms slightly. This deformation alters the electrical resistance of the sensor, and this change is converted into a voltage signal proportional to the applied pressure.
Voltage pressure transducers come in a variety of types, each suited to specific applications. Some popular types include strain-gauge pressure transducers, piezoresistive pressure transducers, and capacitive pressure transducers.
Why Voltage Output Signals?
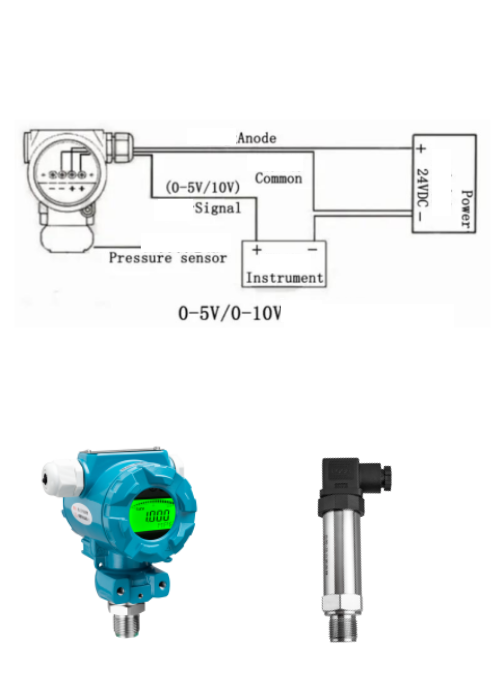
Pressure changes can trigger variations in a sensor’s electrical resistance. In voltage output transducers, these changes convert into a voltage signal that matches the shift in pressure. These voltage signals usually fall within 0-5Vdc or 0-10Vdc, although the range can vary depending on the transducer and its application.
Voltage output signals, common in pressure and temperature sensors, are a type of analog output signal. There are many output options to choose from in this category. The most frequently seen ones in industrial settings are 1-5VDC, 1-6VDC, and 0-10VDC, particularly when power usage isn’t a main concern.
In our growing world of IoT and IIoT, sensors can now run on low power while using less current. This is a big win for remote equipment where replacing batteries often can be expensive and time-consuming.
In response to the demand for low power, various voltage output choices now run on 3V, 3.3V, 3.7V, 5V, and 9V power supplies and batteries. Some common signal pairings with these supply voltages include millivolt, 0.5-2.5VDC non-ratiometric, and 0.5-4.5VDC ratiometric outputs. The 0.5-2.5VDC output option is becoming more popular due to increased usage of 3 to 5VDC lithium-ion batteries.
While millivolt signals are ratiometric, 0.5-4.5VDC output, ratiometric to a regulated 5VDC excitation, is more commonly associated with the term “ratiometric.” This type of signal has gained popularity in automotive and off-road applications because it is proportional to the supply. For instance, a 10% drop in supply from the 5V source would result in a 10% decrease in the output signal. This type of signal continues to be used in similar applications and has also found use in industrial applications like compressors and water pumps.
Voltage Output Wiring Configurations
Voltage output pressure transducers typically come in two wiring configurations: three-wire and four-wire systems.
In a three-wire system, one wire is connected to the positive voltage supply, another to the output, and the third one to the ground. This setup is straightforward and commonly used.
The four-wire system, on the other hand, uses two wires for the supply voltage and two wires for the output. This configuration reduces errors due to voltage drop in the supply leads, providing more accurate readings, especially over longer distances.
Our Top Voltage Pressure Transducer Picks
Applications of Voltage Output Pressure Transducers
- Tank Level Monitoring: Paired with a SCADA system, these sensors are ideal for remotely monitoring fuel or water levels, especially in locations where conserving battery life is essential.
- Oil Field Equipment: In far-flung oilfields, these sensors help conserve battery life while providing ample signal strength for measuring and transmitting data to telemetry units and then to the cloud.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Factories are increasingly adopting IoT technology to measure pressure and temperatures of various equipment, particularly where installing power sources is costly or difficult.
- HVAC and Refrigeration: For HVAC/R installations, these affordable, user-friendly sensors swiftly provide pressure, temperature, and combined readings, making them popular for use in confined spaces like boiler rooms.
- Automotive Systems: In vehicles, these sensors are crucial for monitoring systems like brakes and fuel, delivering real-time data for optimal operation.
- Aerospace and Aviation: These sensors offer real-time measurements in critical monitoring areas such as cabin pressure, engine oil pressure, and hydraulic systems, ensuring safe and efficient flights.
FAQ
Voltage output signals in pressure transducers play a crucial role in pressure monitoring and control. Understanding the workings of these signals and their appropriate applications can help you choose the right transducer for your specific needs.
Remember, at Sino-Inst, we offer a variety of voltage pressure transducers tailored to your requirements. Our experienced team is ready to assist you in finding the best pressure measurement solutions. Reach out to us today!
Request a Quote
Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.
