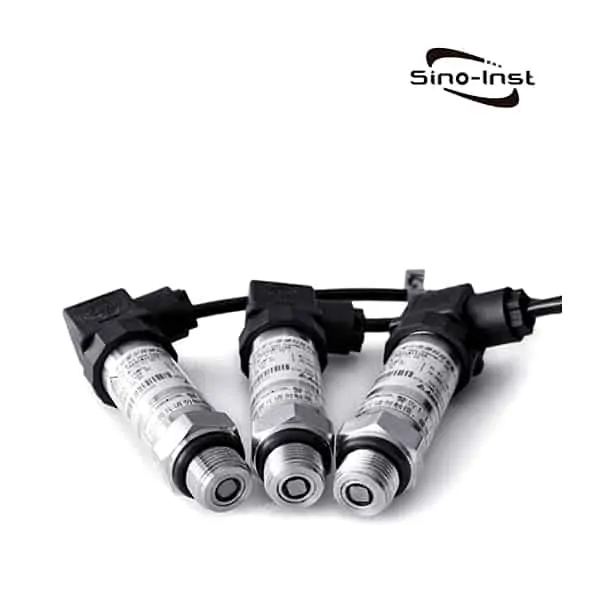
What Is a Fluid Pressure Sensor?
Fluid Pressure Sensors refers to sensors that can be used to measure the pressure of liquid media. Such as measuring pressure of Oil, Fuel and other fluid systems (select a sensor with the appropriate range for your system). Fluid Pressure Sensors are also called liquid pressure sensor or liquid pressure transducer. Fluid Pressure Sensors have important uses. For example, the direct measurement of pressure in a fluid line. For example, put Fluid Pressure Sensors into the liquid, measure the liquid pressure, and estimate the liquid level. For example, by measuring the differential pressure of Fluid, the flow rate of the pipeline can be calculated.

What is a pressure sensor?
Typically, a pressure sensor (sometimes called a pressure transducer or pressure transmitter) is used to measure the pressure of a fluid (gas or liquid).
Pressure is an expression of the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and is usually expressed in force per unit area.
Pressure sensors generate electrical signals related to the applied pressure. Such signals are usually digital or analog, but optical, visual and auditory signals are also common.
Industrial pressure sensors, also known as pressure transducers, pressure transmitters, pressure indicators and pressure switches.
Extended Reading: Smart pressure transmitter working principle
How do fluid pressure sensors work?
An instrument for measuring fluid pressure. Usually the measured pressure is compared to a reference pressure (such as atmospheric pressure or other given pressure), thus measuring the relative pressure or pressure difference.
According to the working principle, it can be divided into three types: liquid column, elastic and sensor.
The principle of the pressure sensor is to convert the pressure signal into an electrical signal. Such as strain type, elastic element deformation caused by resistance change. Piezoelectric, the use of piezoelectric effect.
Various pressure sensors can be miniaturized, more accurate and fast to measure, especially to measure dynamic pressure, realize multi-point inspection, signal conversion, long-distance transmission, computer connection, timely processing, etc., so as to develop rapidly and widely used.
Extended reading : Types of pressure sensors
Applications of fluid pressure sensors
Fluid pressure sensors are mainly used in: construction machinery, hydraulic and pneumatic systems, petrochemicals, energy and water treatment, water conservancy and hydropower, compressors and other fields:
Read more about: Calculation Of Pressure Drop
Pressure Sensor For Liquid Level Measurement
In physics, the pressure P of a liquid is determined by the relationship: p=pgh.
For the same kind of liquid, the liquid density p is constant. Therefore, the pressure P of the liquid is linearly proportional to the height h of the liquid surface (the height from the liquid surface).
It is not difficult to find that the pressure of the liquid at different heights of the liquid level is also different.

As shown in the figure above, when the pressure sensor is used to measure the liquid level, the pressure sensor is installed at the bottom of the tank. When the liquid level in the tank changes, the height h from the tank bottom to the liquid level also changes at the same time, and the pressure naturally changes accordingly, thus achieving the purpose of continuous measurement.
One of the advantages of using pressure sensors for liquid level measurement is non-contact. Compared with mechanical and static methods, when measuring, it does not require too many parts to contact the liquid, and the installation is relatively convenient.
In addition, in terms of measurement principle, compared with similar non-contact measurement methods such as laser and ultrasonic, the relationship of pressure sensor measurement principle is simpler and linear, and it is more intuitive in data processing, analysis and processing.
Extended reading: Differential pressure level transmitter working principle
Pressure Sensors For Flow Measurement
The pressure of the fluid is an extremely important parameter in flow measurement. Differential pressure flowmeter uses the pressure difference at both ends of the throttling element to realize flow measurement.
In addition, the working pressure of the flowmeter can be known through pressure measurement, and necessary correction calculations are performed to ensure the accuracy of flow measurement.
Extended reading: flow rate and pressure relationship
Differential pressure flow meter advantages and disadvantages
Upstream and Downstream Flow Straight Pipe Requirements-for Flowmeter Installation

fluid depth pressure sensor
If we make the pressure sensor into a submersible sensor, it can be used to measure the depth of the liquid.
The most common fluid depth pressure sensor is what we often call the submersible hydrostatic pressure sensor. Used to measure the depth or level of liquids such as water, fuel.
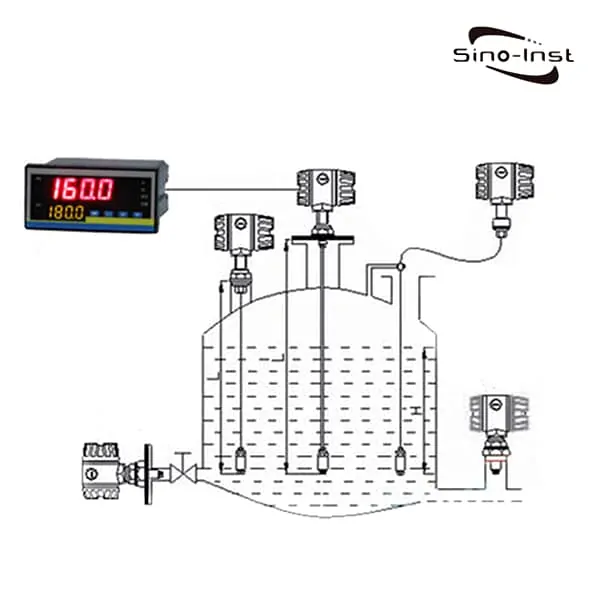
Hydrostatic level measurement is often used for tank level measurement. Hydrostatic level measurement is one type of continuous level measurement.
Hydrostatic pressure sensors are used to measure the level or fill height of liquids. Hydrostatic pressure measurement is suitable for liquid level measurement due to the static pressure effect of non-flowing fluids. This physical principle describes the effect of the gravity of a stationary (i.e. non-flowing) liquid on the measurement point. This gravity is often described as “hydrostatic pressure”.
Related pressure transmitter
Related Pressure Measurement Solutions
Frequently
Asked
Questions
Sino-Inst offers over 50 pressure sensors for fluid measurement. About 50% of these are differential pressure flow meters, 40% is the liquid pressure sensor, and 20% are pressure Level Transmitter.
A wide variety of Fluid Pressure Sensors options are available to you, such as free samples, paid samples.
Sino-Instrument is a globally recognized supplier and manufacturer of pressure measurement instrumentation, located in China.
Request a Quote

Wu Peng, born in 1980, is a highly respected and accomplished male engineer with extensive experience in the field of automation. With over 20 years of industry experience, Wu has made significant contributions to both academia and engineering projects.
Throughout his career, Wu Peng has participated in numerous national and international engineering projects. Some of his most notable projects include the development of an intelligent control system for oil refineries, the design of a cutting-edge distributed control system for petrochemical plants, and the optimization of control algorithms for natural gas pipelines.












